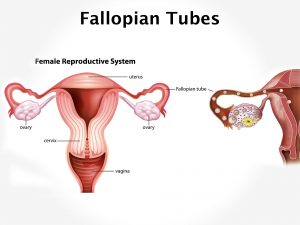
Causative & risk factors
Dysmenorrhea is caused due to the uterine contractions that take place during menstruation to remove the dead and old endometrial tissue out of the body through the vagina.
Primary dysmenorrhea occurs in healthy women with no underlying medical condition. It occurs as a result of prostaglandin imbalance.
Secondary dysmenorrhea occurs in women with an underlying medical condition such as ovarian cysts, pelvic inflammatory disease, endometriosis, fibroids, STDs etc.
Clinical presentation
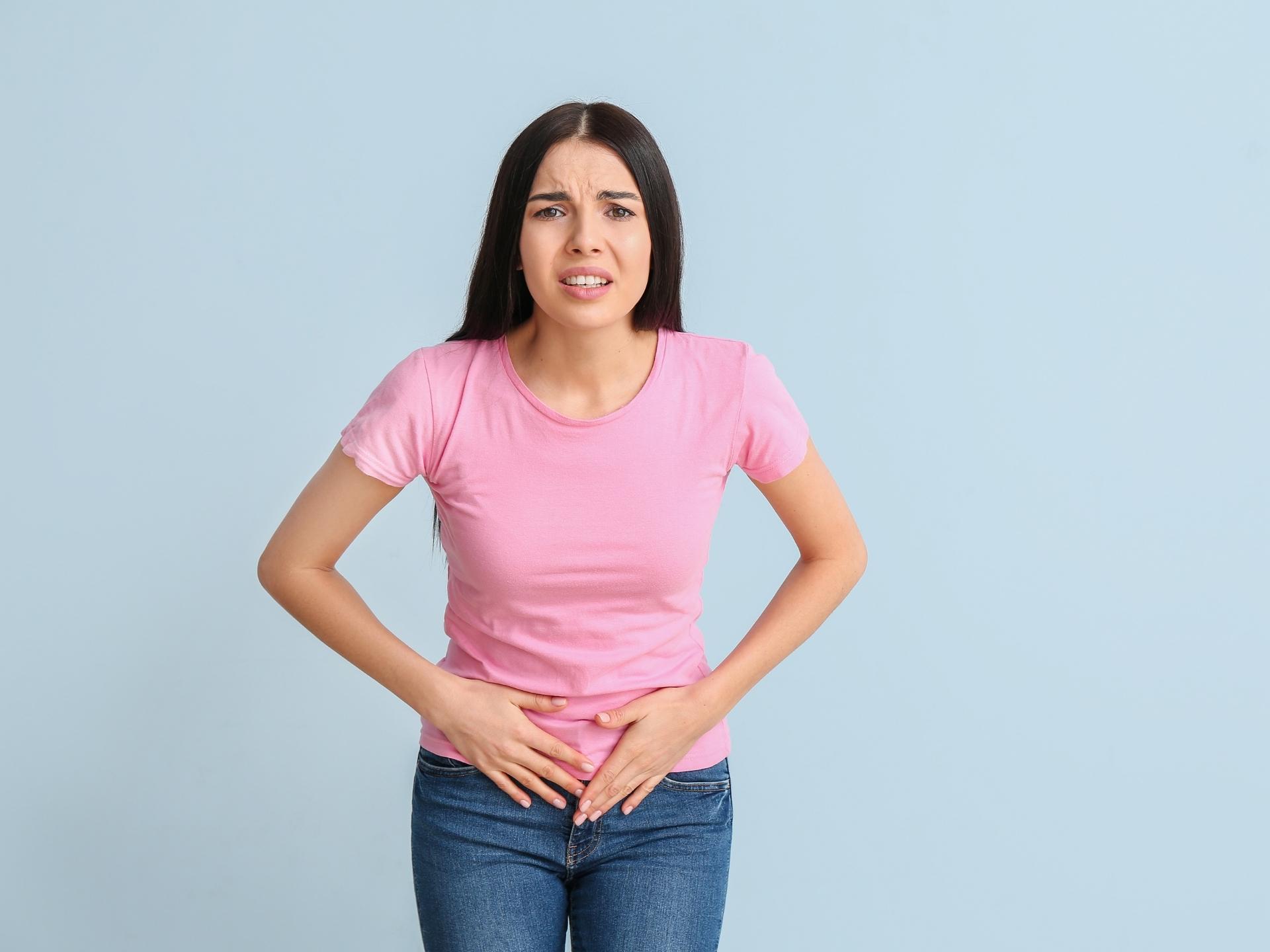
Before or during each menstrual period; the woman experiences mild to severe pain in the lower abdomen. The pain may radiate to the hips, thighs or the back.
Dysmenorrhea may be associated with other symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, hot flushes, fatigue etc.
Investigations
The diagnosis of dysmenorrhea can be made on the basis of presenting symptoms. Certain tests such as a complete blood count and a pelvic ultrasound may be carried out to rule out other causes of abdominal pain. Occasionally laparoscopy may be indicated if the cause is unclear.
Treatment
During an attack of dysmenorrhea, several simple measures can help to relieve the pain. Taking a warm shower, using a heating pad, massaging the belly area etc is helpful. Making certain lifestyle changes such as eating healthy, exercising regularly, practicing Yoga and intake of specific dietary supplements are helpful in reducing the duration and severity of dysmenorrhea. Medications like pain killers and anti-inflammatory drugs are useful to relieve the pain. Alternative therapies like Homoeopathy and Ayurveda offer a good scope in treating dysmenorrhea.
In cases of secondary dysmenorrhea, the underlying cause of the pain must be assessed and treated accordingly.
Recent updates
Research has revealed that using the drug sildenafil citrate vaginally helps to relieve menstrual cramps in their acute phase.





![Lobular Carcinoma In Situ [LCIS]](https://moho.loopshell.com/read/wp-content/uploads/2022/01/Lobular-Carcinoma-In-Situ-Lcis-300x300.png)