Causes and risk factors
Factors responsible for ectopic pregnancy are increased incidence of chronic pelvic inflammatory disorder, tubal plastic operations, tubal reconstructive surgery, ovulation induction, history of induced abortion, IUD use, and intrapelvic adhesion following pelvic surgery. Factors delaying migration of fertilized ovum into the uterine cavity and factors facilitating nidation of fertilized ovum in the tubal mucosa result in tubal ectopic pregnancy.
Clinical presentation
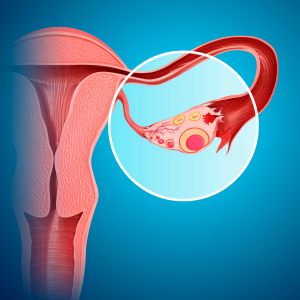
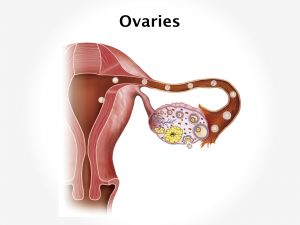
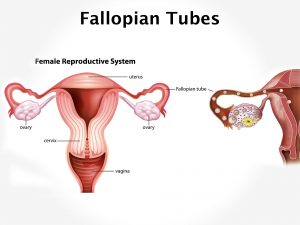
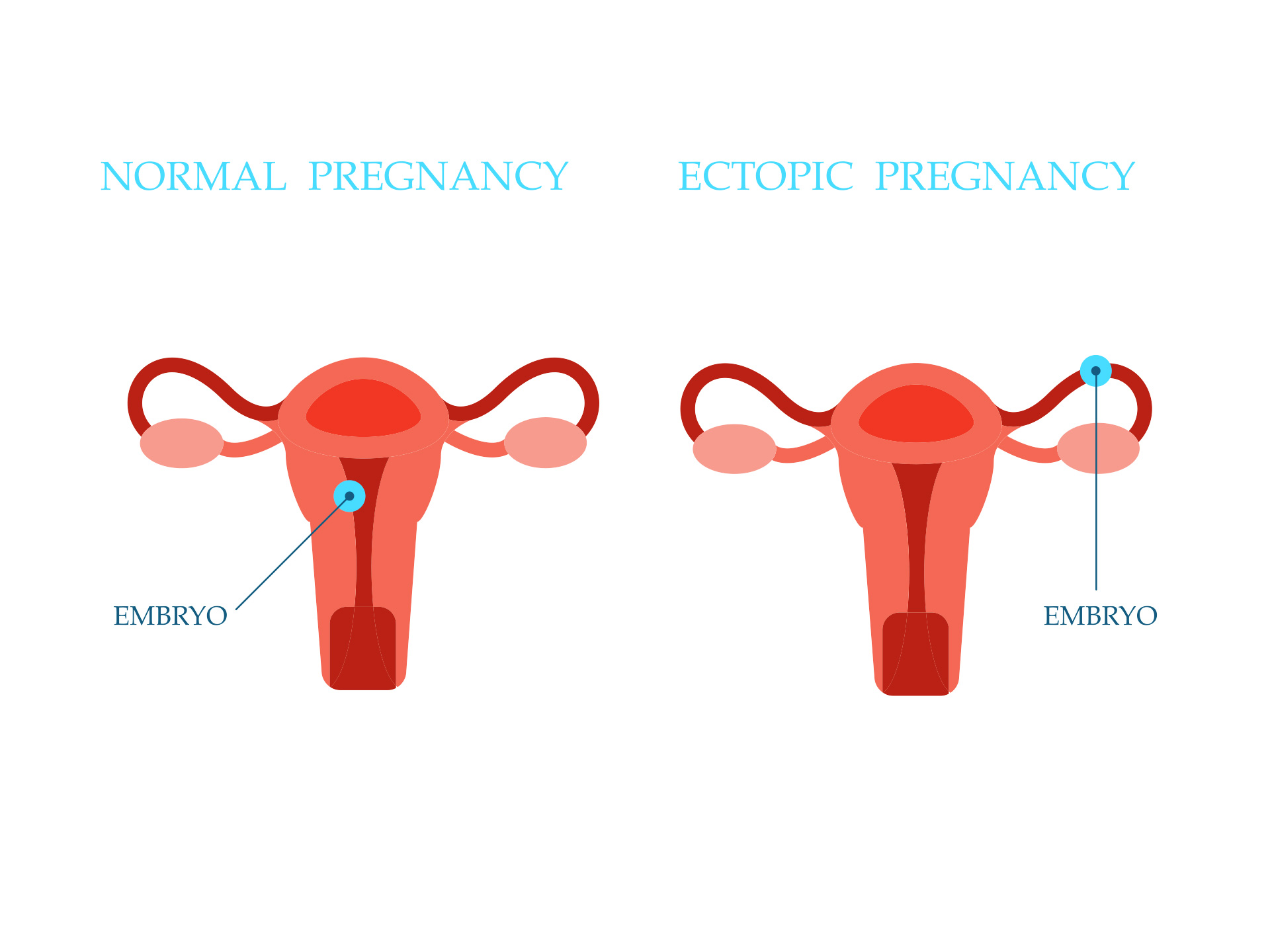
Implantation sites of fertilized ovum in an ectopic pregnancy can be either extra uterine or uterine. Extra uterine implantation include tubal, ovarian, or abdominal. Tubal pregnancy can occur in the ampulla, isthumus, infundibulum, or interstitial. Abdominal sites can be intraperitoneal or extraperitoneal. Uterine site involves cervical, angular or corneal.
Clinical features include 3 types acute, unruptured, or chronic. Classic picture of acute ectopic pregnancy includes short period of amenorrhoea, followed by abdominal pain, vaginal bleeding followed by dizziness. Unruptured tubal ectopic involves delayed period or spotting with features suggestive of pregnancy, uneasiness on one side of flank. Chronic ectopic has an insidious onset. It presents as amenorrhoea of 6-8weeks, lower abdominal pain, vaginal bleeding, bladder irritation, rectal tenesmus, and fever due to infection. Period of ectopic pregnancy lasts from 5 to 12 weeks. Earlier the diagnosis, better the treatment. Ruptured ectopic pregnancy is clinical emergency where patient presents with pain in abdomen, vaginal bleeding, dizziness or unconsciousness with signs of shock.
Investigation
Medical history by the patient and Clinical examination by the gynaecologist helps in diagnosis. Bimanual examination of cervix may be extremely painful and reveal ill defined mass. UPT to confirm pregnancy, routine Blood tests, ESR; serum progesterone, serum HCG level. Transvaginal sonography, colour Doppler sonography will reveal ectopic pregnancy.
Treatment
Medication [drug methotrexate] to terminate the pregnancy is helpful in case the ectopic pregnancy is diagnosed early. In other cases it is treated with a laparoscopic surgery. In case of heavy bleeding, tubal rupture laprotomy may be recommended. Ectopic pregnancy if not well treated can lead to maternal death.
Facts and figures
Prevalence of ectopic pregnancy ranges from 6 to 16 %. Incidence has increased during mid twentieth century. It was 20 per 1000 pregnancies in 1990s. The most common extra uterine site is the fallopian tube which constitutes 98% of all the ectopic pregnancies.




![Lobular Carcinoma In Situ [LCIS]](https://moho.loopshell.com/read/wp-content/uploads/2022/01/Lobular-Carcinoma-In-Situ-Lcis-300x300.png)