Causes and risk factors
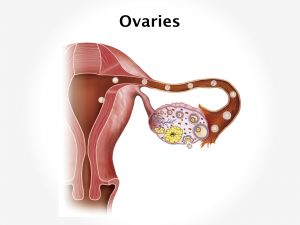
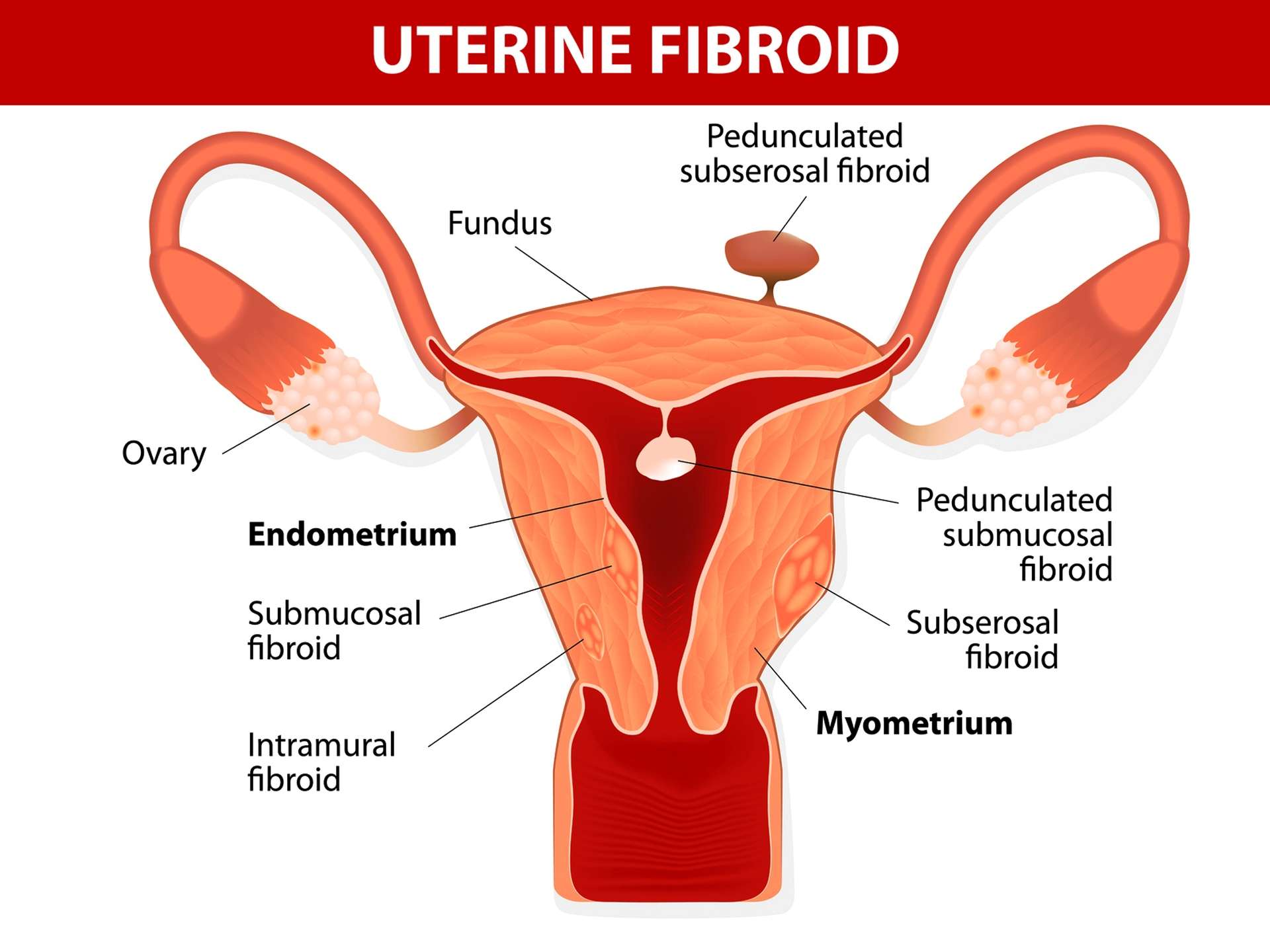
The exact cause of cancer is not known, but various risk factors or predisposing factors have been put forth. It is found that the cells undergo an uncontrolled and abnormal proliferation which gives rise to formation of tumors. Genetic predisposition is one of the major causes. Hereditary plays a major role. People with weak immune system are more prone for cancer. Women having early menarche and late menopause is more prone for developing endometrial cancer. Estrogen therapy increases the risk. Various conditions like obesity, diabetes, polycystic ovarian diseases, ovarian tumors, endometrial hyperplasia contribute to the risk factors. Secondary affection of uterus i.e. metastasis from cancer present elsewhere in the body can also occur.
Clinical presentation:
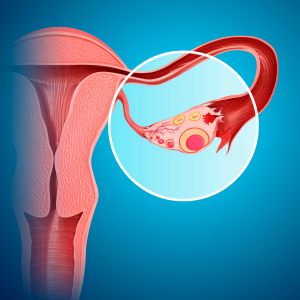
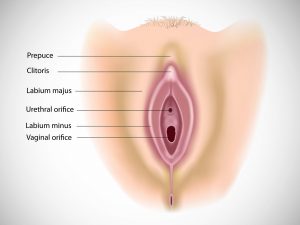
Endometrium cancer is asymptomatic in its early stage. Later as the diseases advanced. Pelvic pain is experienced by the patient. The pain can be dull aching to severe and crampy such that it can hamper the daily routine of the women. Bleeding which is unusual or profuse bleeding or bleeding for many days is seen. Pain during sexual intercourse and also while bowel movement or during urination. Aleterd bowel movement, nausea, vomiting long with bloated feeling in the abdomen is seen. On examination tenderness a palpable mass in the pelvic region along tenderness is seen. Weight loss, fatigue, loss of appetite is the other associated symptoms seen.
Investigations:
Diagnosis is done of the basis of the symptoms narrated by the patient and the recto vaginal examination carried out by the gynecologist. Hysteroscopy for internal visualization of the uterus is done. Biopsy is the diagnostic investigation. Trans vaginal or abdominal sonography, cystoscopy, proctoscopy, CT scan can be done. In addition to these Routine blood, CA 125 blood test, ultrasonography, and MRI scans are advised for metastasis.
Treatment:
Depending upon the extend and stages of cancer the treatment is planned. Various surgical approaches can be adopted. Hysterectomy is found to be effective in cases where metastasis has not occurred. Radiation therapy is used. Targeted chemotherapy and immunotherapy agents are administered.
Other Modes of treatment:
Certain other modes of treatment can also be helpful in coping up the disease. Taking into consideration the symptoms in holistic way, homoeopathy can offer a good aid for the relief of the symptoms.
Recent update:
European Society of Endocrinology has published an article stating that aggressive forms of endometrial cancer are linked to high levels of a specific protein within cancer cells.




![Lobular Carcinoma In Situ [LCIS]](https://moho.loopshell.com/read/wp-content/uploads/2022/01/Lobular-Carcinoma-In-Situ-Lcis-300x300.png)