Causes and risk factors
The cause of exfoliative dermatitis in most cases is unknown. In remaining cases, the cause is usually aggravation of underlying skin disease or drug reaction. Skin disease associated with exfoliative dermatitis is seborrheic dermatitis, atopic dermatitis, contact dermatitis, psoriasis, pityriasis rubra pilaris, ichthyosis, lichen planus, cutaneous T-cell lymphoma.
Clinical presentation
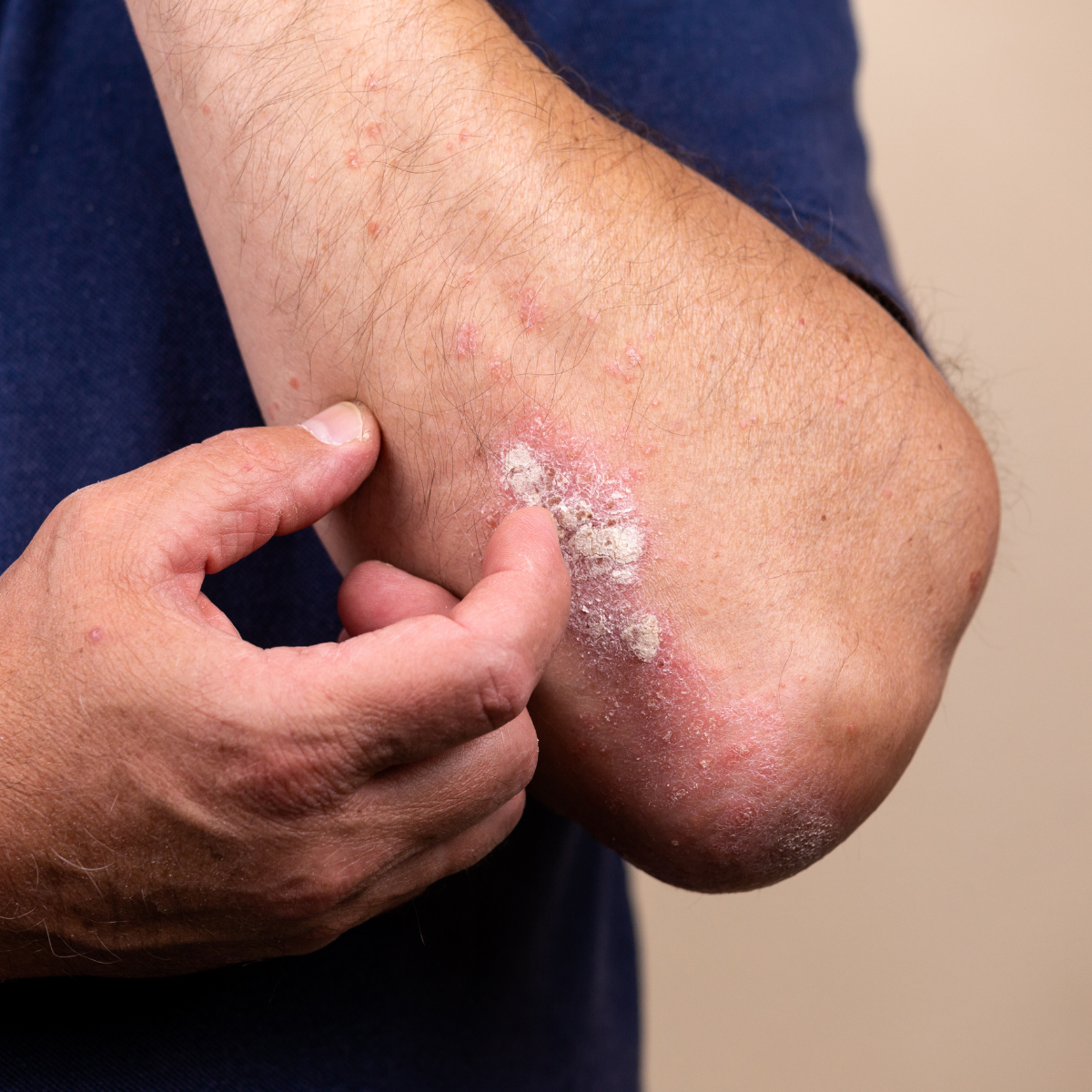
Exfoliative dermatitis is exfoliation or shedding of skin due to some underlying condition causing itching of skin. There is thickening, generalized skin redness and swelling followed by peeling of the skin. Nails become thick and ridged. There is thickening of the palms of hand and soles of feet. Pigmentary changes are observed. Loss of fluids and proteins through the damaged skin occurs. Fever with chills, secondary infections, swollen lymph nodes, and increased heart rate is seen in severe cases.
Investigation
Medical history by the patient and clinical examination by the dermatologist helps in diagnosis. Skin biopsy is recommended.
Treatment
Exfoliative dermatitis is a medical emergency and requires immediate hospitalization. Treatment will depend upon the underlying cause. General care consists of cessation of all unnecessary medications. Antibiotics are given for underlying infection, antihistamines for severe itching, and intravenous fluids to replace the fluid loss. Wet wraps, emollients, and topical steroids to maintain skin moisture can contribute further to the treatment.
Other Modes of treatment
The other modes of treatment can also be effective in treating exfoliative dermatitis. Homoeopathy is a science which deals with individualization and considers a person in a holistic way. This science can be helpful in combating the symptoms. Similarly, the Ayurvedic system of medicine which uses herbal medicines and synthetic derivates is also found to be effective in treating exfoliative dermatitis.