Causes and risk factors
As the name suggests, exposure to high levels of fluoride is the major contributing factor. This exposure can be acute or chronic one. Chronic high levels of exposure to fluoride particularly through drinking water (above 1.5 mg/litre of water as per WHO) for a prolonged period can lead to excessive accumulation of fluoride in body causing fluorosis. Ingestion through food or exposure to industrial gases can also initiate complaints. Although rare, accidental drinking of contaminated water can lead to acute complaints. Use of fluorine rich toothpaste can lead to damage to the teeth. Dental fluorosis is commonly seen in children if the intake has been excess before formation of permanent teeth.
Clinical presentation:
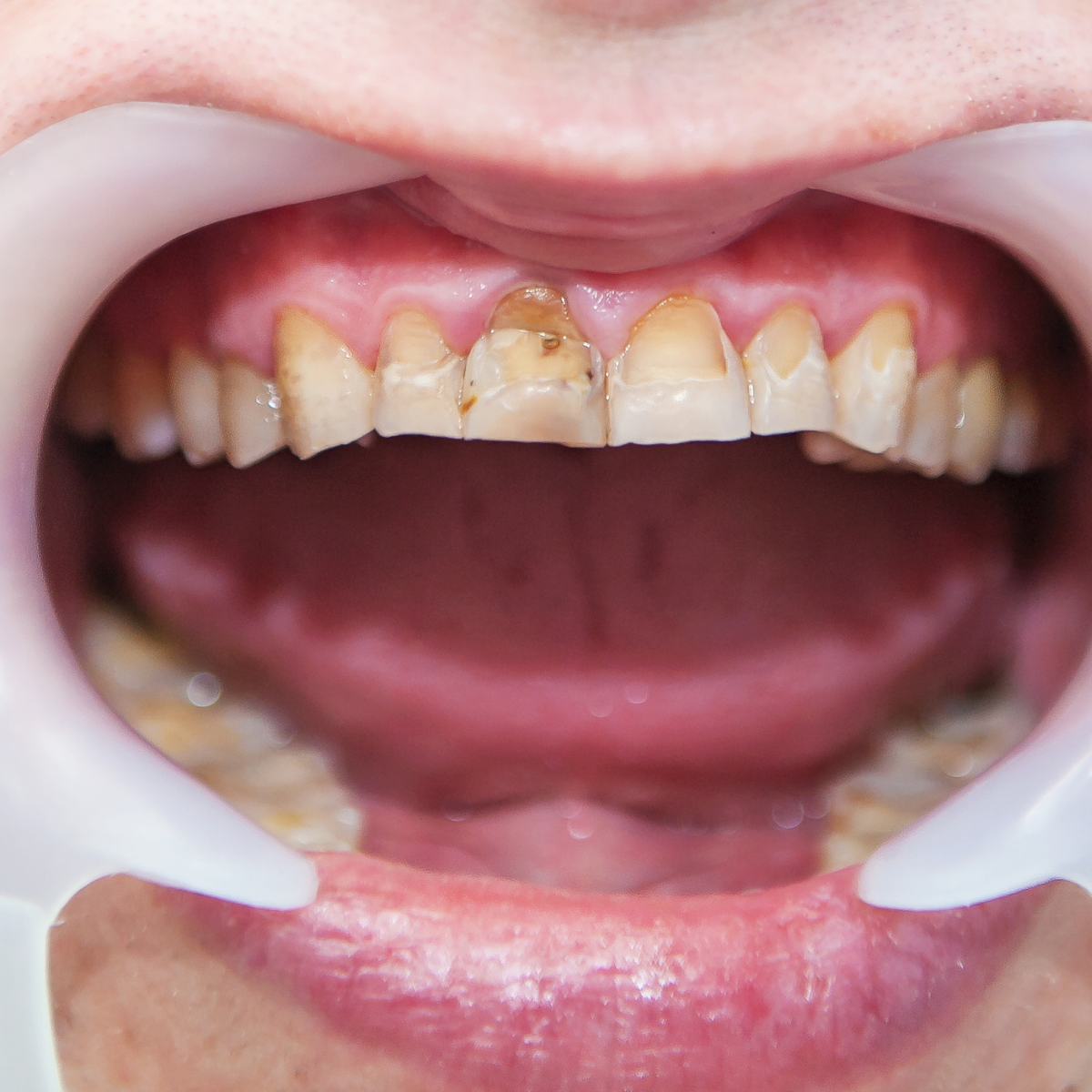
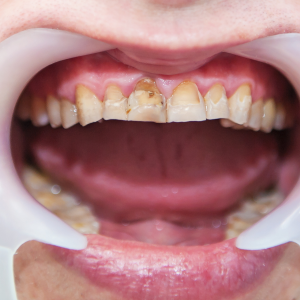
Excessive accumulation of fluorine can lead to complaints pertaining to skeletal system along with dental complaints. Affection of teeth due to excess of fluorine is called as dental fluorosis. In skeletal fluorosis, the patients complain of pain in the back and various joints. Loss of sensation in limbs along with stiffness in various joints and back region is seen. In severe cases, the bone structure is affected and calcification of ligaments can occur. It can lead to complications like spastic paraparesis and anemia. In acute poisoning, an individual can come up with complaints of nausea, vomiting, pain in abdomen, increased salivation, muscle spasm, and even seizures. Dental fluorosis is characterized by loss of enamel, pitting and staining of teeth.
Investigations:
Considering the complaints narrated by the patient, a physical examination of the patient is carried out. Opinion of a dentist is must in case of teeth complaints. X-ray of the bones and serum fluoride levels are the investigations done. Urine analysis for fluoride levels can be done. In severe cases, bone biopsy can be advised.
Treatment:
Defluorination of water is the foremost step which needs to be adopted, and a matter of public health issue. Cases with minimal complaints recover over time. In acute poisoning cases, the patient needs medical attention and hence is hospitalized and appropriate treatment is started. In case of dental fluorosis, teeth cleaning or whitening can be done. Veneers can be used in cases where the cosmetic appearance of teeth is severely damaged. Drinking safe water with safe minimal levels of fluoride is of foremost importance.
Facts and Figures:
As per WHO statistics, fluorosis affects millions of people around the world, but as regard to dental fluorosis, the very mild or mild forms are the most frequent.