Causative and risk factors
The common organisms responsible for development of folliculitis are staphylococcus, pseudomonas, streptococci and sometimes pityrosporum (yeast).
The primary cause of folliculitis is shaving, especially when infected blades are used. Profuse sweating, injuries or excessive coverings onto the skin can also cause folliculitis. Pre-existing skin conditions such as dermatitis, acne etc. or use of long term antibiotics or topical corticosteroid creams predispose to folliculitis.
Lowered immunity due to HIV, diabetes mellitus etc, increases one’s risk of developing folliculitis. Other risk factors include obesity and frequent exposure to hot water baths.
Clinical presentation
Folliculitis is more commonly seen in certain areas of the body such as beard and moustache areas in males, anterior portion of legs, axillary or pubic region and the scalp.
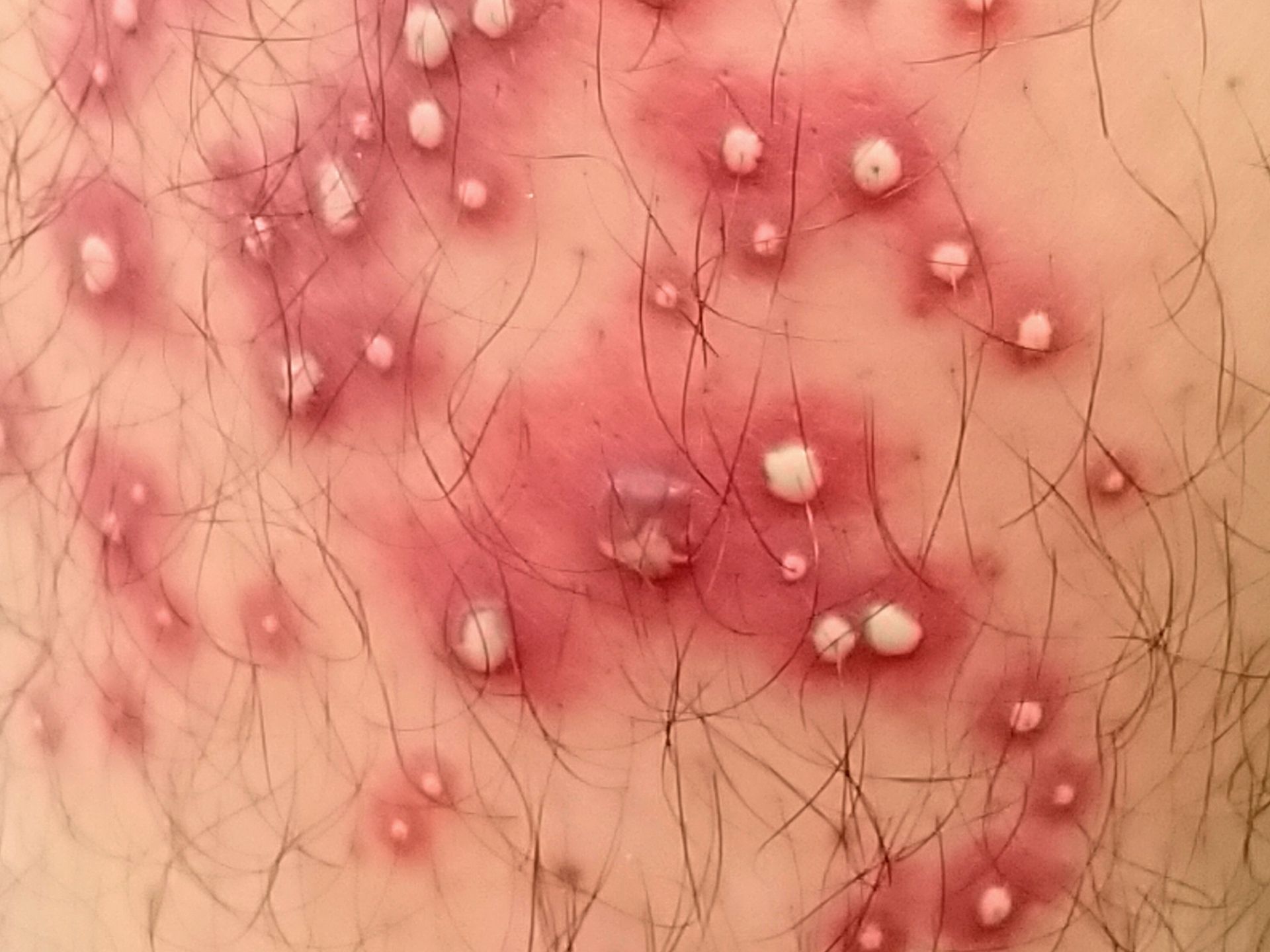
Folliculitis presents as pimples located around a hair follicle. Infected follicles may be 1 or many in number and itching is present. The lesions may drain pus, blood or other fluids. Fever may be present.
Folliculitis can give rise to complications like furunculosis, permanent loss of the affected hair and scarring of the underlying skin.
Diagnosis & Investigations
Diagnosis can be made on the basis of physical inspection of the lesions. Microscopic examination of the fluid collected from the lesion is sometimes recommended. Rarely biopsy of the lesion is advised.
Treatment
Most cases of folliculitis will heal without treatment in a span of a few days.
Hot fomentation of the affected area helps to drain the follicle. Medicated shampoos can be used for folliculitis of the beard or scalp.
Oral or topical antibiotics are prescribed. Antifungal ointments are given if a fungal infection is suspected.