Causes and risk factors
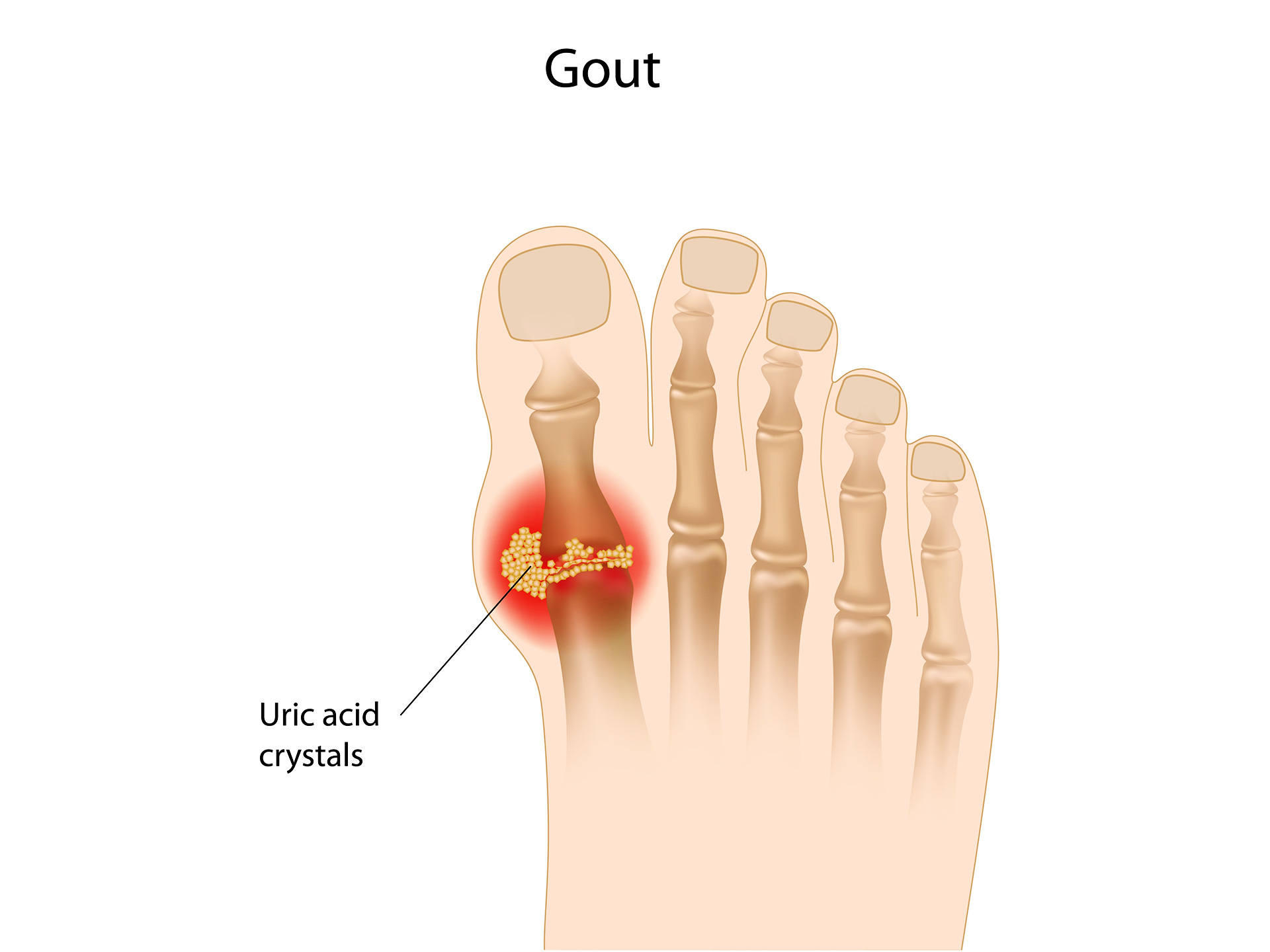
Uric acid is one of the waste components of blood. High levels of uric acid in the blood is called as hyperuricemia .Hyperuricemia is stamped only when the serum and plasma urate concentration is more than 7.0mg/dl in male and more than 6.0mg/dl in females. When the levels of uric acid increase in the blood it undergoes the process of formation of solid crystals know as monosodium urate which then settles in and around the joints. From these crystals nodules which are called as “tophi” are formed which are responsible for the bone deformity. High levels of urates are caused due to less excretion of uric acid by kidney, dietic errors and certain genetic factors. Some of the other provocating factors are alcohol intake in excess, Food containing high amount of uric acid (meat, shell fish), obesity, and diabetes. Stress and use of certain drugs can also predispose gout. Gout is not only caused by increase accumulation of uric acid but also due to impaired excretion of uric acid.
Clinical presentation:
The most common joints affected are metatarsopharangeal joint(big toe) ,knee, ankle, foot and hand joint. At times patient can remain asymptomatic and the high level of uric acid in blood can be incidentally detected. The attack is profound and mostly occurs at night. The red strand features of gout are heat, redness and swelling of the joints, pain in joints and mild fever along with chills. Over tunes the skin over the joint undergoes desquamation. The duration of acute attacks may vary. In some the subsequent attack may never occur, some might suffer from the attack frequently. However in such cases the number of sites and severity may increase. The acute attacks of gout when is unattended by a proper medical care can lead to formation of painless tophi leading to permanent deformities of the joints. High levels of uric acid can also lead to renal calculi and high blood pressure. The pain and stiffness caused can also hamper the day to day activity thus rendering the person feeling irritable and depressed.
Investigations:
Diagnosis is done of the basis of the symptoms narrated by the patient and the physical examination carried out by the doctor, big toe appearance in acute attacks is helpful. High levels of serum uric acid levels are diagnostic. Synovial fluid examination is recommended. Certain investigations which can be done are X-ray, MRI or CT scan of the affected joint. Routine blood test and a profile of specialized blood test are done to rule out other diseases.
Treatment:
The medications are prescribed with an intention to prevent the attack, to reduce the serum and urine uric acid concentration and to increase the excretion of uric acid. . Non steroidal anti inflammatory drugs (NSAID), steroids, DMARDS (Diseases modifying anti rheumatic drugs) and pain relieving drugs are prescribed. In severe cases corticosteroid injections and topical pain relieving gels and lubricants are advised. Surgical intervention is not needed in gout. Change in the diet is essential. Food substances which high purine content should be avoided. The foodstuffs of high purine,uric acid content are red meat, pulses, and whole grain cereals. Crash diets should be avoided. Even certain drugs after the consultation of the doctor should be avoided e.g. thiazide diuretics.
Other Modes of treatment:
Certain other modes of treatment can also be helpful in coping up the symptom. Taking into consideration the symptoms in holistic way, homoeopathy can offer a good aid for the relief of the symptoms. The Ayurvedic system of medicine which uses herbs and synthetic derivates can also be beneficial in combating the complaints. Acupuncture which is the science of insertion of fine needles on the certain stimulating spots on the body has proved to be effective. Certain yoga exercises can also be helpful in relieving the pain and strengthening the muscles.
Recent updates:
A new study presented at the European League against Rheumatism Annual Congress (EULAR 2014) reveals that most of the men who suffer from gout also struggle with erectile dysfunction (ED), which is frequently severe.