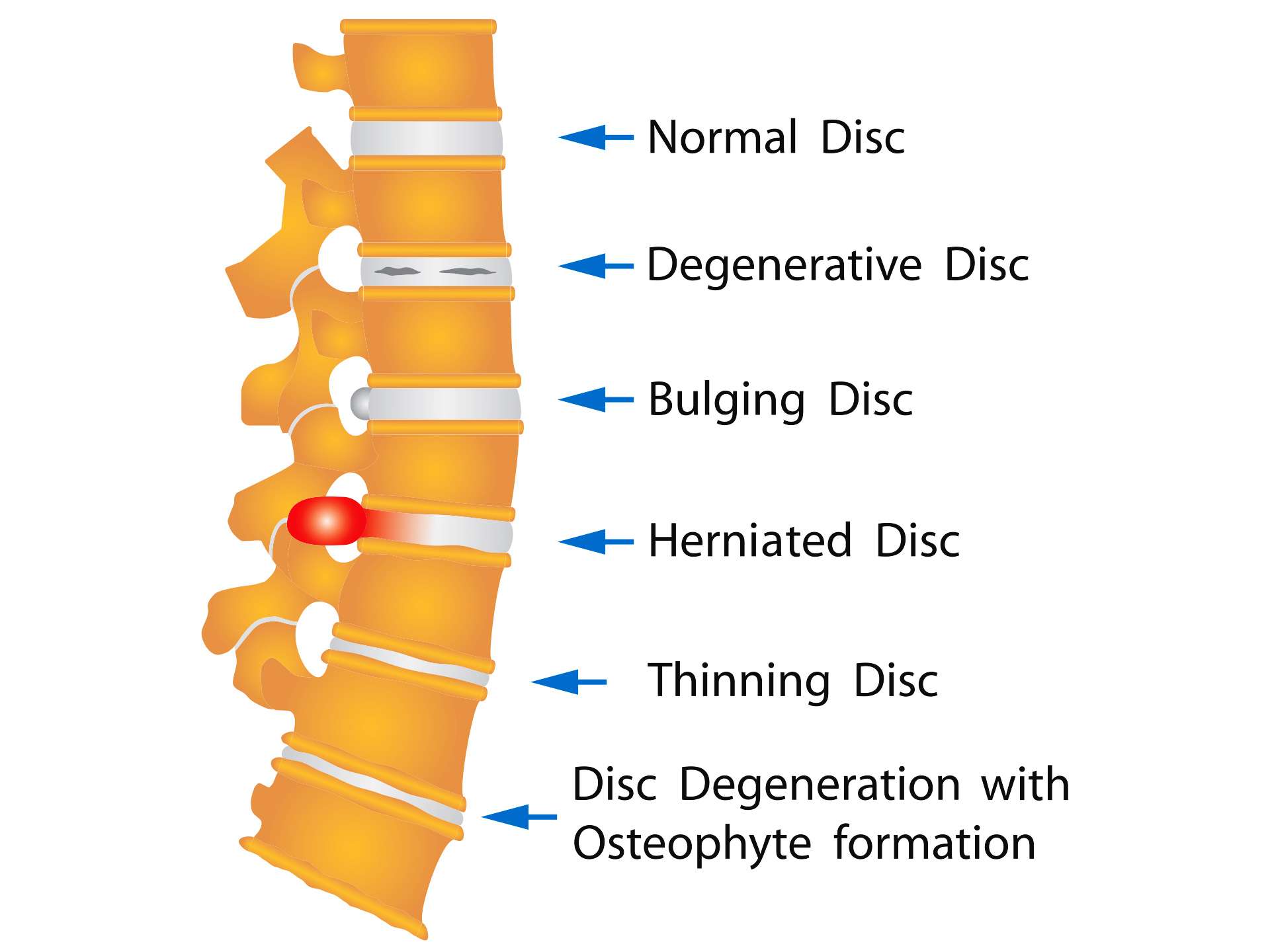
Causes and risk factors
A herniated disc occurs when the inner part of the disc bulges through a weakened outer part of the disc. This may compress nearby nerves or the spinal cord causing pain and discomfort. Herniated disc is often caused by aging related wear and tear; this is called as disc degeneration. Due to disc degeneration the outer ring of the disc becomes weak or torn and allows the inner portion to slip out. Ageing causes the spinal discs lose some water content, which makes them weak and less flexible. Herniation may also cause pressure on the adjacent nerves. Other causes may include twisting or turning to lift a heavy object, weak muscles, sedentary lifestyle, trauma – a blow or injury to back. Risk factors include bring overweight, people with 35 to 45 years old of age.
Clinical presentation
Many times patient is asymptomatic .Some people with herniated disc may not have any symptom, but some herniated disc can be painful. Herniated disc mostly occur in lower back [Lumbar spine] but they may also occur in neck [Cervical Spine]. The most common symptom is pain, often presents as low back pain or neck pain, which radiates to mostly one side of the body. It radiates to the arms and/or legs and worsens after standing or sitting for long time, while sneezing, coughing, or laughing, while bending backward or walking more than a few yards. Unexplained muscle weakness, tingling, numbness, aching, or burning sensations in the affected area may be associated with herniated disc.
Investigation
Medical history by the patient and Clinical examination by the orthopaedic doctor helps in diagnosis. X-rays, Computerized tomography [CT scan], Magnetic resonance imaging [MRI], Myelogram will help in further evaluation of the disease.
Treatment
No treatment is required for asymptomatic patients. Treatment depends on the level of discomfort and the extent to which the disc has slipped out of the place. It involves medications like pain relief medicines [analgesics], NSAIDs, narcotics, muscle relaxing medicines, steroids. Physiotherapy treatment which includes exercises, traction, electrical stimulation, short-term bracing for the neck or lower back will also help in managing herniated disc. In severe cases surgery is advised [discectomy] where a portion of protruding disc is removed.
Other Modes of treatment
The other modes of treatment can also be effective in treating herniated disc. Homoeopathy is a science which deals with individualization considers a person in a holistic way. This science can be helpful in combating the symptoms. Similarly the ayurvedic system of medicine which uses herbal medicines and synthetic derivates are also found to be effective in treating herniated disc.