Causative & risk factors
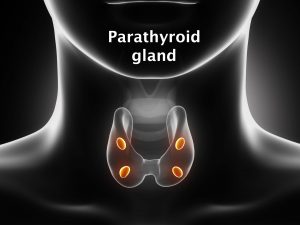
Hypoparathyroidism can be caused due to:
- Surgical removal or damage to the parathyroid gland
- Presence of antibodies against the parathyroid gland
- Absence of the parathyroid glands since birth
- Low magnesium levels in the blood
- Radiation therapy in the neck region
Since the levels of parathyroid hormone are deficient, the calcium levels in the body decrease significantly (hypocalcemia) and the levels of serum phosphorus increase (hyperphosphatemia).
Clinical presentation
Most of the symptoms arise as a result of low calcium levels in the blood and bones. There is pain and spasms in the muscles and joints and the bone density is low. Numbness and tingling is present in the fingers and toes. The hair and skin are dry and the nails are brittle. The patient is fatigued with an impaired memory, reduced consciousness and anxiety. Other symptoms include dysmenorrhea, abdominal pain, headaches, seizures, cataract and teeth problems.
Investigations
Blood tests will be performed to check the levels of calcium, phosphorus, magnesium and parathyroid hormone.
The urinary calcium levels will be tested.
Treatment
The focus of treatment is to restore the calcium and phosphorus balance in the body. The initial treatment is taking calcium carbonate and vitamin D supplements. Doctor may recommend eating a high-calcium (beans, almonds, apricots, oats etc) and a low-phosphorus diet.
In some cases, your doctor may prescribe diuretics, to help decrease the calcium levels excreted in urine. If your calcium levels are life-threatening, then the doctor will give calcium intravenously.
Recent updates
Studies are being done to assess the efficacy and safety of giving parathyroid hormone to patients of hypoparathyroidism.