Causative & risk factors
Environmental conditions like heat and moisture when combined with derangement in health favor the growth of fungus; and these opportunistic fungi causes skin infection, particularly in the genital area.
Wearing tight undergarments and/or excessive sweating in the genital area are major risk factors for development of jock itch; more so if these conditions persist for a long time. Using public shower or locker rooms are breeding grounds for spread of fungal infections. Obese people and those suffering from diabetes or immune-compromised patients have a higher risk of developing jock itch.
Jock itch can also occur as a result of spread of an existing athlete’s foot infection. This is because the fungus responsible for both the infections is the same.
Clinical presentation
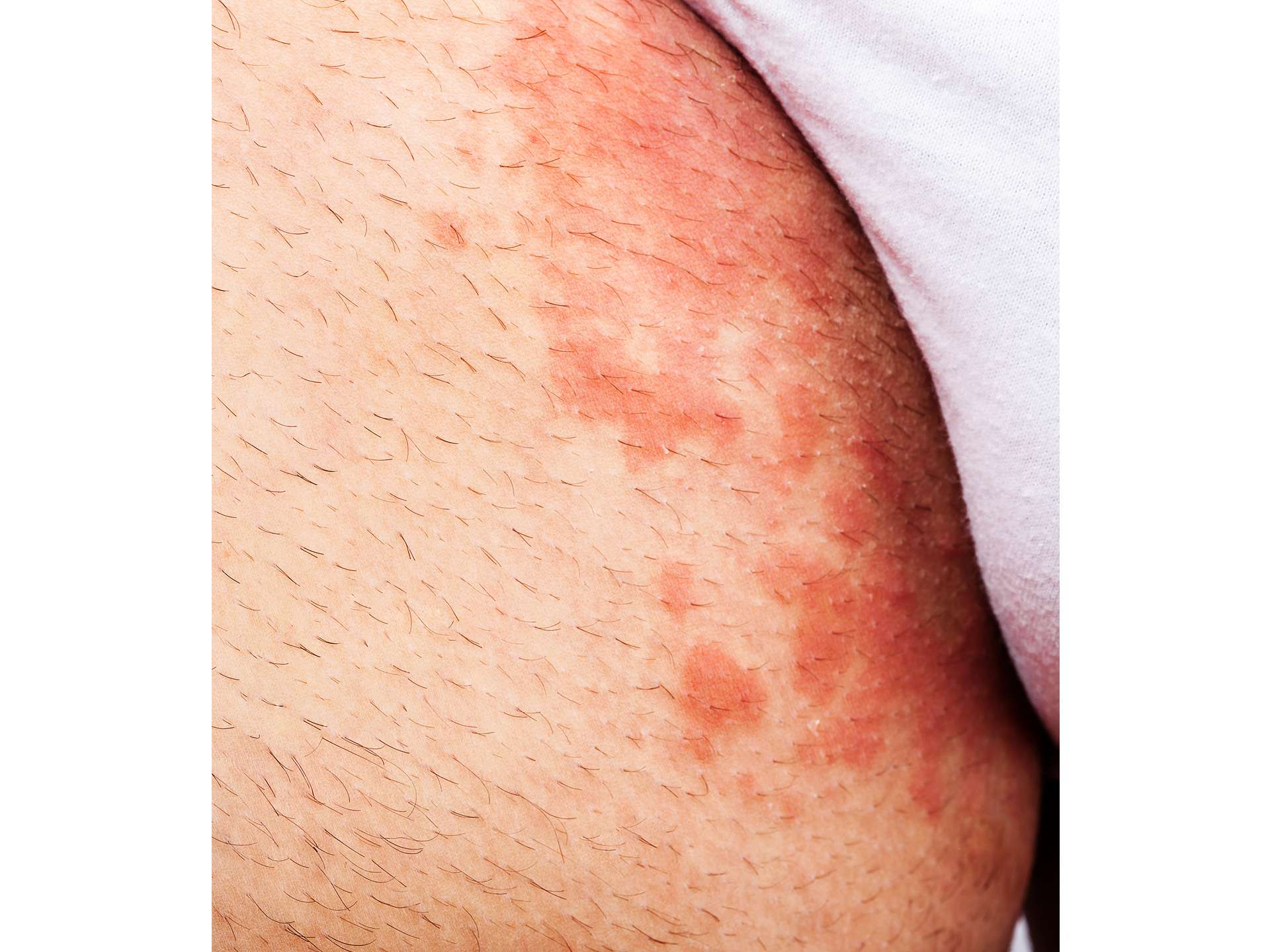
Intense itching at the groin region is the chief symptom. Red skin rashes are present primarily in the groin region and may spread to buttocks, abdomen and thighs. Lesions are usually not found on penis and scrotum. Rashes have defined edges and the central area of the rash is reddish brown and scaly. Rashes are lined by small bumps that may look like blisters. Blisters may ooze pus or clear fluid. Burning and pain sensation may be present at groin region. There can be peeling, scaling, cracking or flaking of skin.
Investigations
Jock itch can be easily diagnosed on the basis of symptoms and physical examination by a physician. It does not require any laboratory tests for diagnosis. Sometimes a physician may take a sample of the affected skin for microscopic examination.
Treatment
The patient is treated with local application of anti-fungal ointments, powders or sprays. Severe cases may need oral anti-fungal tablets. If secondary bacterial infection is present, antibiotics are also prescribed. The patient is instructed to practice good personal hygiene habits such as wearing well-fitted undergarments, changing them frequently, keeping groin area dry, washing thoroughly after using public restrooms etc.