Causes and risk factors
Unlike other cancers, the cause of Kaposi’s is known. Viral infection due to Human herpes virus 8 is the major causative factor for Kaposi’s sarcoma. Those suffering from HIV infection and homosexuals are more prone to such cancers. There are several types of Kaposi’s sarcoma – endemic type (AIDS related); classic type (Mediterranean), endemic type (African), and iatrogenic Kaposi’s sarcoma.
Clinical presentation:
In Kaposi’s sarcoma, the abnormal proliferation of the cells start at one part of the body and then spreads to the other part. The tumors are found below the skin surfaces; membranes of mouth and nose and then spread to other organs like liver, stomach, intestine, etc. Formation of a lesion is a striking feature of Kaposi’s sarcoma, lesions having a bruise like appearance – red or brown tumors or formation of nodules are seen. These lesions are mostly seen in legs and face. The symptoms may vary as per its location. Appearance of lesions in lungs can lead to difficulty in breathing and shortness of breath. It can cause blockage of the airways, while those appearing in stomach can lead to gastric complaint of pain in the abdomen, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. The stools can be black and bloody. Over time blood loss can lead to anemia. Weakness and fatigue are the other associated complaints seen.
Investigations:
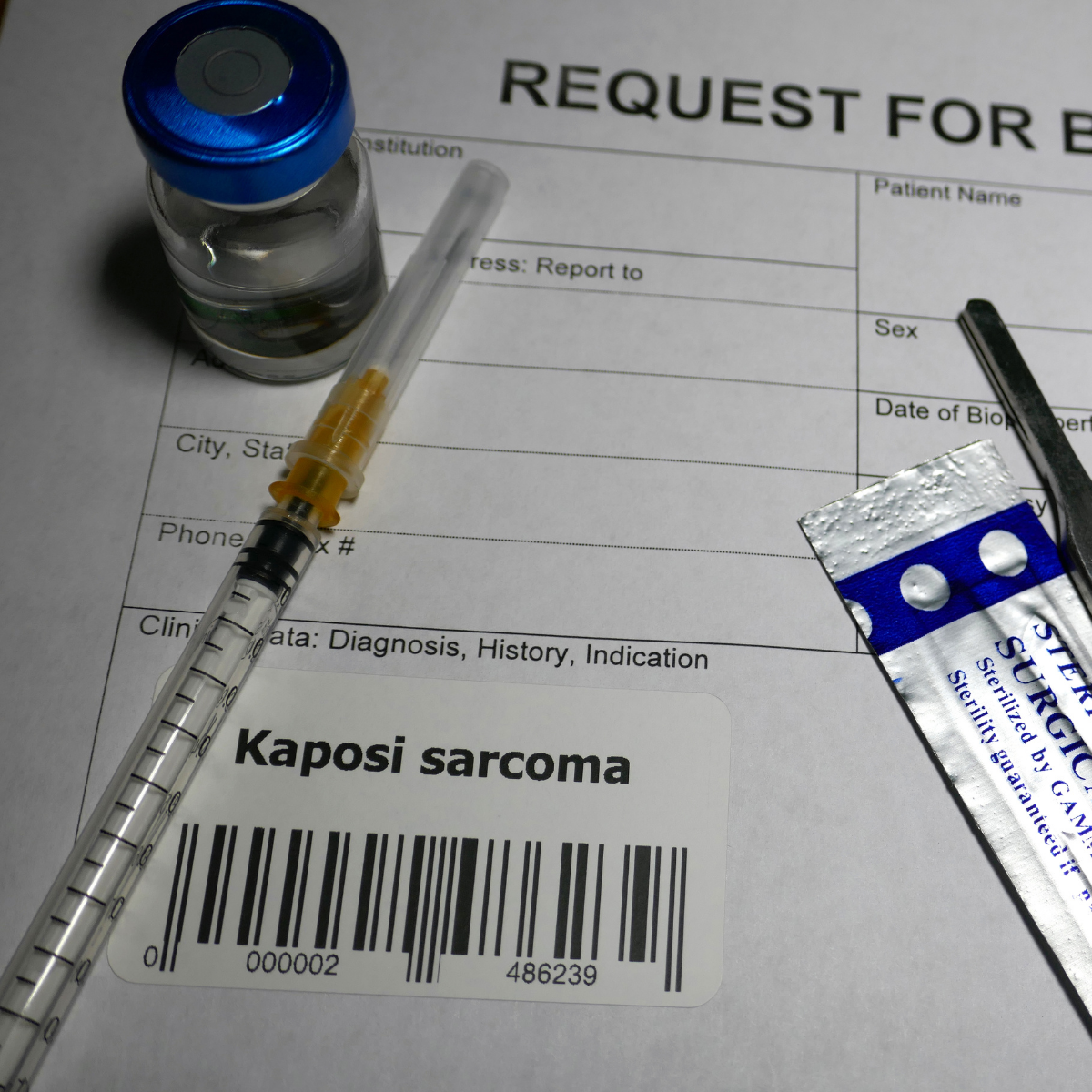
Taking into consideration the complaints mentioned by the patient, a physical examination of the patient is carried out. Local examination of the skin is carried out. Accordingly, certain set of investigations are advised. Barium x-ray, endoscopy, bronchoscopy, or CT scan of lungs and abdomen are done. If any abnormal growth or mass is detected, a biopsy is done. Other routine investigations can also be advised.
Treatment:
When detected in early stages, Kaposi’s sarcoma can be easily treated. Highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) is the effective method of treatment. In cases of skin lesions, local therapy and radiation treatment is adopted. Systemic chemotherapy is indicated in cases of involvement of the internal organs. Biological therapy is the choice of treatment adopted in HIV patients.
Recent update:
Researchers are going on to find new ways for treating Kaposi’s sarcoma.