Causes and risk factors
In most of the cases, the children present with knock knees by the age of 3-4 years as the legs are folded in the womb during pregnancy, later gradually the lower extremities can straighten up. However, in a few cases the lower extremities remain curved. These are known as knock knees. However, as the age advances the legs straighten up. In certain cases knocked knees are caused due to a bone deformity which is inherited or can be due to some rare genetic conditions. Rickets, deficiency of vitamin C, osteomyelitis, osteoarthritis, and rheumatoid arthritis are certain other contributing factors. Obese and overweight people are more prone towards developing this condition. Unilateral knock knee is seen in cases of shinbone injury.
Clinical presentation:
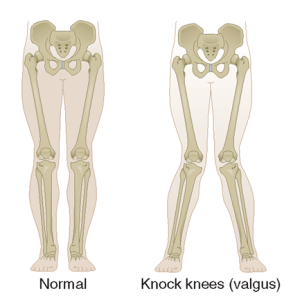
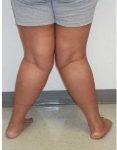
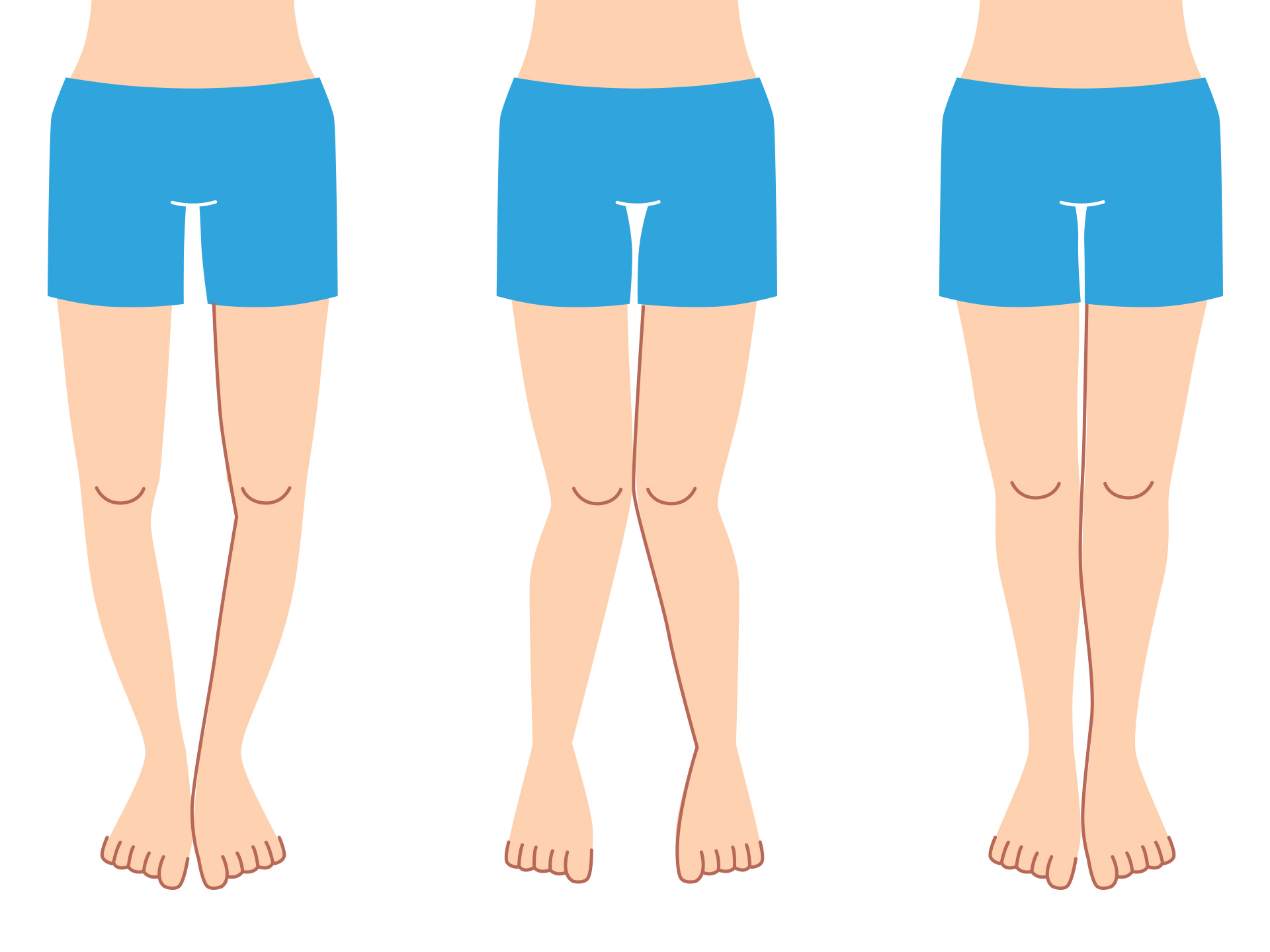
Either one or both the legs can be affected. Curving of the legs with large gaps between the ankles or feet is the main feature seen. Usually the gap between the ankles is more than 10 cm. On standing, straight curving of the knee is seen and a big difference is seen between the angle of the legs. This curving of legs leads to pain in knees, dull aching pain is felt. The pain is aggravated while walking and movement, hence walking becomes difficult. The patient can start limping. This can also lead to social embarrassment which can lead to isolation and low self-esteem. Certain other complaints pertaining to the underlying cause can also be seen.
Investigations:
Diagnosis is done on the basis of the symptoms narrated by the parents along with clinical examination carried out by the orthopedic doctor. Certain physical tests are carried out. The distance between the ankle and knee is measured. Along with this the height of the child is taken into consideration. The leg, hip, and knee alignment and gait are considered. X-ray can be done. Advanced imaging techniques like MRI or CT scan can also be done.
Treatment:
The complaint of knock knees usually resolve by the age of 6-7 years, hence no medical intervention is needed. If the complaints persist and patient complains of pain in the knee, then pain reliving medications are advised. Modification in shoe is recommended. Use of brace is advised. Surgical intervention is needed in cases if the complaint persists beyond childhood.
Other modes of treatment:
Certain yoga exercises or physical exercises under a trained physiotherapist will help to strengthen the muscles and ligaments and improve the flexibility.
Complications:
Knock knees can lead to poor posture which can gradually affect the other parts of the body like hip, back, and feet.
When to contact a doctor:
Contact an orthopedic doctor if one experiences any abnormality in the knee and ankle along with pain and difficulty in walking.
System involved: Musculoskeletal system
Organ involved: Nerves, bones, knee, ankle, back