Causative & risk factors
The commonest cause of laryngitis is a viral infection. Occasionally it may be due to a bacterial infection. Excessive overuse of the voice (talking, singing etc) can aggravate laryngitis. Exposure to irritants like alcohol, smoking (including secondhand smoke) and air pollutants are also common causes of laryngitis, especially chronic. Other causes include GERD, a severe cough, chronic sinusitis, injury or surgery in the neck region, presence of tumors and vocal cord paralysis.
Clinical presentation
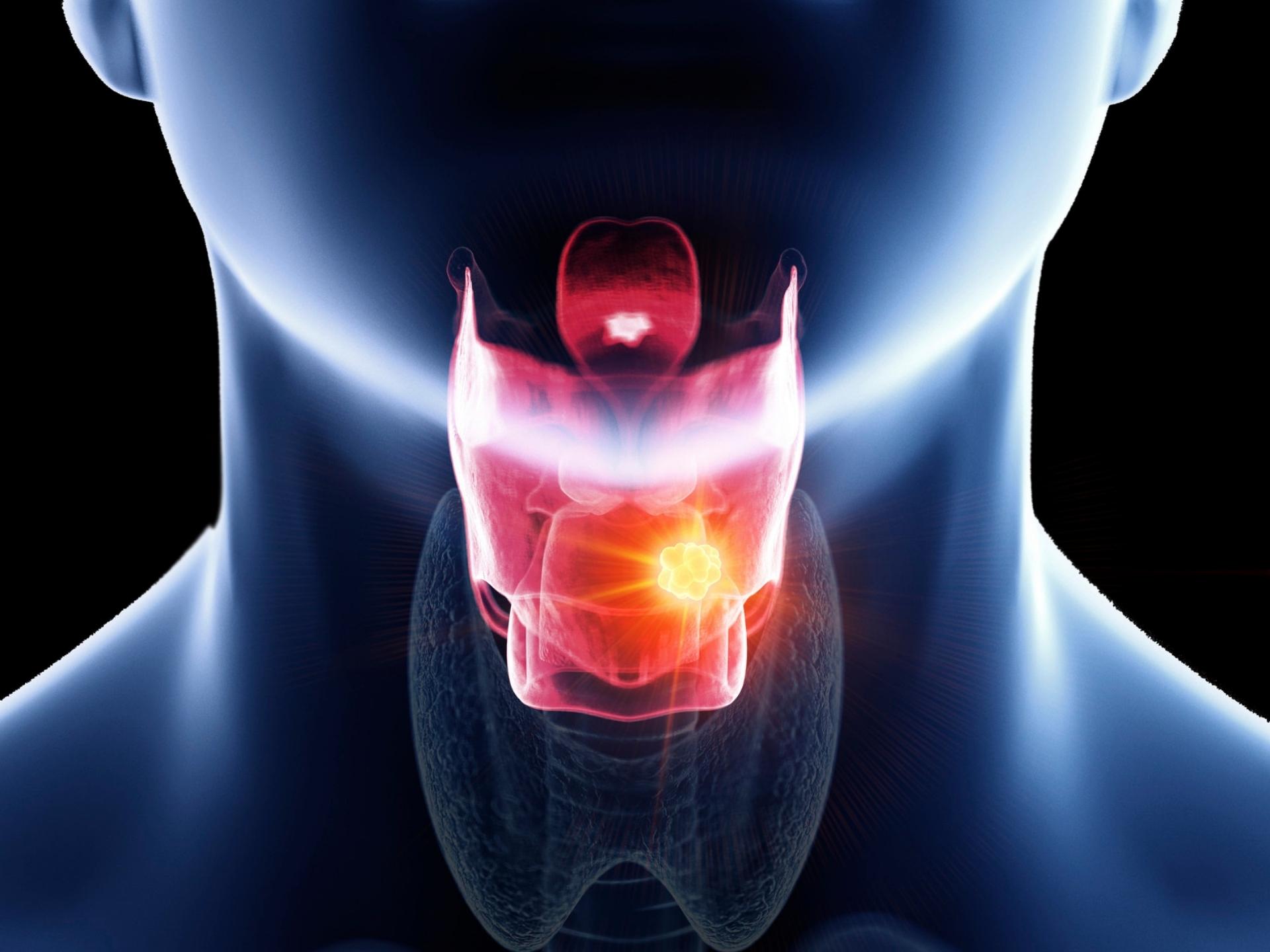
Hoarseness of voice is usually the first symptom to appear, followed by a cough and fever. The patient may also suffer from soreness and tickling sensation in the throat. The lymph nodes in the neck area may appear swollen.
Investigations
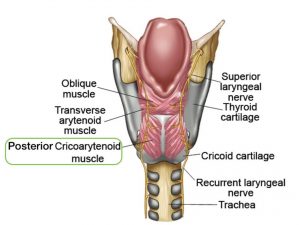
Laryngitis can be diagnosed on the basis of the patient’s symptoms. A laryngoscopy may be performed. Very rarely, a biopsy of the laryngeal tissue may be done especially if nodules or other suspicious growths are seen.
Treatment
The most important treatment for laryngitis is resting your voice for several days until complete recovery takes place. During this period, singing and talking loudly are prohibited whereas soft speech is permissible. Antibiotics are given only it the cause of laryngitis is a bacterial infection. Anti-inflammatory drugs can be given in severe cases or patients who urgently need to regain their voice for a short period.