Causes and risk factors
Lobomycosis is caused due to infection with the fungi named Lacazia loboi. Infection occurs after scratch or insect bites.
Clinical presentation
The skin lesions commonly develop over arms, face, ear, and extremities. Small hard nodules resembling keloids appear on the skin. Burning and itching of the lesions may be present. Sometimes they are hyperchromic with flat surface. Over a period of time it spreads. Older lesions become verrucoid and may ulcerate.
Investigations
Medical history by the patient and clinical examination by the doctor helps in diagnosis. Skin biopsy is required.
Treatment
Antifungals are used, but are generally ineffective. Surgical excision or cryosurgery is the first line of treatment. Antifungals and anti-leprosy drugs after surgery help to delay the recurrence of lesions.
Complications
Complications such as secondary bacterial infection in the ulcerated lesion can occur.
When to Contact a Doctor
One must consult a doctor if there is an unusual persistent skin infection which is unable to resolve with antifungals.
Prevention
There is no sure way to prevent lobomycosis.
Systems involved
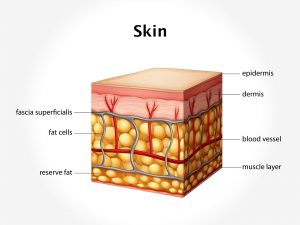
Integumentary system
Organs involved
Skin of arms, face, ear, and extremities