Causes and risk factors
Macrodontia can be caused due to some unknown etiology. However, commonly it is associated with certain conditions. Macrodontia is one of the characteristic features seen in KBG syndrome. Hemifacial hyperplasia in which enlargement of the tissues of bones of one side of the face and head occurs, also causes macrodontia. Pituitary gigantism is another common hormonal disorder which can cause macrodontia.
Clinical presentation:
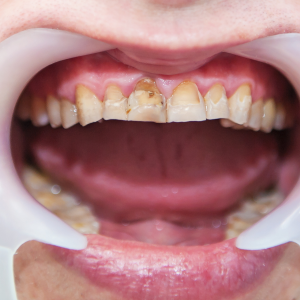
The tooth is abnormally large as compared to another tooth. Depending upon the teeth involved, it is classified as localized, true generalized, and relative generalized type. In true generalized type, all the teeth in mouth are large. In relative generalized one, the teeth are normal or may be slightly large, but the main cause is a small jaw. While in localized macrodontia, one tooth on the same side is large as compared to others. Hampering the cosmetic appearance is one of the main complaints caused by large tooth. The inequality of teeth causes uneven bites, and as a result, chewing is affected. Improper chewing causes various gastric complaints. Pain in face and skull area can also occur. Inequal size of tooth can also lead to difficulty in cleaning and as a result such teeth are more prone to oral cavities.
Investigations:
Clinical examination carried out by the dentist is usually sufficient to diagnose the case; however, along with this an oral x-ray can also be advised.
Treatment:
The affected large tooth can be scaled back to normal size. However, extraction can also be done. After extraction, the natural tooth is replaced with artificial tooth or prosthesis. Along with this, pain relieving medications can also be advised. In case of dental caries, cleaning and filing is needed.