Causes and risk factors
Meconium is the stool passed by the neonate soon after birth or a few days after birth. In some cases, the baby passes stool while still in uterus. This stool gets mixed with the amniotic fluid in the amniotic sac and is inhaled by the fetus causing MAS. Experts believe that meconium is released in the amniotic fluid when the baby is under stress during the process of labor. Factors that can cause stress to the baby are long labor, pregnancy that has crossed the expected date of delivery, complications during pregnancy such as diabetes (gestational diabetes) or hypertension (PIH), decreased oxygen to the fetus, placental insufficiency, oligohydraminos, drug abuse by pregnant woman. MAS involves different pathophysiologies like airway obstruction, surfactant dysfunction, inflammation, lung oedema, pulmonary vasoconstriction, and bronchoconstriction.
Clinical presentation
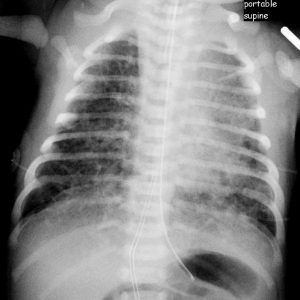
When the baby inhales meconium, it traps the baby’s airways thus causing difficulty to breathe. The newborn baby presents with rapid or difficult breathing after birth. Bluish discoloration of the skin (cyanosis) is seen. There is dark green appearance of the amniotic fluid and baby’s skin. There is reduced heartbeat. Barrel shaped chest is evident. Abnormal breath sounds are heard during auscultation.
Investigations
Medical history by the patient and clinical examination by the doctor helps in diagnosis. Abnormal breath sounds during physical examination are diagnostic. Apgar score is measured. Arterial blood gas test is required to check percentage oxygen and carbon dioxide in the infant. Chest x-ray is recommended.
Treatment
Meconium aspiration syndrome is a medical emergency. As soon as the diagnosis is confirmed – suction of the aspirated meconium, oxygen support if the baby is not breathing and has a low heart rate, is required. Other supportive treatment includes antibiotics to treat infection, breathing support using ventilator, warmer to maintain body temperature. In severe cases, extracorporeal membrane oxygenation is needed.
Complications
Complications such as pneumothorax, persistent pulmonary hypertension, pulmonary edema of the newborn can occur.
When to Contact a Doctor
Since the condition is present at birth, doctor will take appropriate measures as soon as MAS is suspected.
Prevention
Reducing stress during pregnancy, avoiding conditions which will cause high blood pressure may prevent the conditions like MAS.
Facts and figures
6% to 25% of infants have meconium stained amniotic fluid, but only 11% develop MAS.
Systems involved
Respiratory system, CNS of the newborn.
Organs involved
Lungs, brain