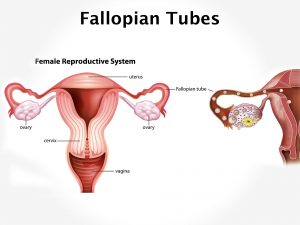
Causes and risk factors
The exact cause of placenta previa is not known. Implantation of embryo in the lower uterine segment can be one of the cause for growing placenta which fails to migrate to upper segment during the advancement of pregnancy .However certain risk factors have been put forth like advance maternal age, smoking, previous history of placenta previa or recurrent abortions, surgery on uterus.
Clinical presentation:
Placenta previa can be partial, marginal or whole (major) depending on obliterating cervix. Complaints are more commonly seen during the second trimester. Intermittent episodes of vaginal bleeding are the hallmark of placenta previa. The bleeding can be scanty or profuse. It is bright red in color. There is no associated pain, however in some cases the women feels contracting pains. Placenta previa can lead to complications like hemorrhages (Internal or external during active labor) creating more complications to the fetal health.
Investigations:
Diagnosis is done of the basis of the symptoms narrated by the patient and the investigations advised by the gynecologist. Abdominal or transvaginal ultrasonography is the diagnostic investigation.
Treatment:
Complete rest in cases of placenta previa is the most essential measure to be adopted. In cases of severe bleeding blood and plasma volume replacement is done. In cases if the baby is mature and there does not exist any danger to the life of the mother and baby then immediate delivery is suggested section is adopted to deliver the baby even if the growth is not complete. Symptomatic treatment to control bleeding is done.





![Lobular Carcinoma In Situ [LCIS]](https://moho.loopshell.com/read/wp-content/uploads/2022/01/Lobular-Carcinoma-In-Situ-Lcis-300x300.png)