Causative & risk factors
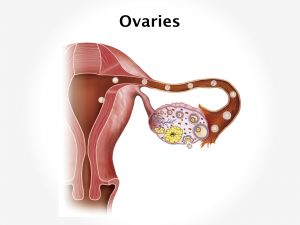
Premature ovarian failure can occur due to depletion or disruption of the ovarian follicles.
Follicle depletion can occur as a result of chromosomal defects, radiation therapy or chemotherapy. Viral infections and exposure to chemicals or toxins can also result in depletion of follicles and hence premature ovarian failure.
The exact cause of follicle dysfunction is not known; it could be due to an autoimmune disorder.
Clinical presentation
Premature ovarian failure results in early onset of typical menopausal symptoms such as absent or irregular periods, hot flashes, low libido and vaginal dryness.
However this condition is different from menopause. IN menopause, there is complete cessation of menses and the woman cannot conceive. In premature ovarian failure, periods stop temporarily and can return. The woman can still conceive.
The biggest complication of premature ovarian failure is infertility, especially when it occurs at a younger age. The affected women may develop osteoporosis as a result of a sudden dip in estrogen levels.
Investigations
A woman with absent periods is first asked to undertake a pregnancy test. Once that is negative, other tests are carried out to detect the cause of infertility. Under metabolic diseases like diabetes and thyroid disorders must be ruled out. The levels of hormones in the blood are tested – follicle stimulating hormone, estradiol and prolactin. Genetic testing can be done to find chromosomal abnormalities.
Treatment
Hormone replacement therapy is suggested to prevent estrogen deficiency and the symptoms arising therewith.
Calcium and vitamin D supplements are recommended to prevent loss of bone density.
Women facing infertility can opt for assistive reproductive techniques such as IVF (in-vitro fertilization) in order to conceive.




![Lobular Carcinoma In Situ [LCIS]](https://moho.loopshell.com/read/wp-content/uploads/2022/01/Lobular-Carcinoma-In-Situ-Lcis-300x300.png)