Causes and risk factors:
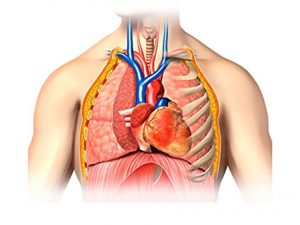
The pulmonary valve is located at the between the right ventricle and pulmonary artery. The deoxygenated blood flows from right ventricle to the pulmonary artery and through the pulmonary artery it carried to the lungs for oxygenation. The pulmonary valve prevents this back flow of blood from the lungs to the right ventricle. In an individual suffering from pulmonary atresia the pulmonary valves possess some abnormality, as a result of which the valve does not open up and the blood from the right ventricle does not flow to the lungs. The exact cause of pulmonary atresia is not known. Certain genetic abnormalities or chromosomal defect contribute to the causation. It is seen hereditary in some children. Children suffering from genetic disorders are more prone for developing pulmonary atresia.
Clinical presentations:
The symptoms of pulmonary atresia is seen during first few hours or days after the child birth. Rapid breathing is seen in baby. On examination bluish discolorations of the skin of the lips, fingers and toes occur. The baby is irritable and the mother finds difficulty in feeding. On touching the baby. It is cold and clammy. As the child grows pulmonary atresia can lead to complications like endocarditis, stroke, delay in development and even heart failure.
Diagnosis and investigations:
Symptoms narrated by the parents along with examination carried out by the pediatrician will help in confirming the diagnosis. Echocardiogram, ECG and X-ray of the chest are the diagnostic investigations recommended. Cardiac catheterization is diagnostic
Treatment:
The baby is kept under medical attention. Ventricular assistance for breathing is given. Intravenous administration of prostaglandin E1 drug is done which will help to prevent the closure of ductus atresiosus. Via cardiac catherisation balloon valvotomy or atrial septostomy or stent replacement is done. In cases of ventricular septal defect cardiac surgery is carried out. . Shut replacement, valve replacement, Hemi fontan procedure of Fontan procedure is done.
Facts and Figures:
The incidence of pulmonary atresia is 1 in 10000 live births.