Causes and risk factors
SA node in right atrium is responsible for sending signals for rhythmic contractions of muscles of heart. Disturbance in this function leads to irregular contractions called arrhythmia. The most common cause of sudden cardiac arrest is arrhythmia such as ventricular fibrillation. Irregular impulses cause the ventricles to contract uselessly , which causes failure of ventricles to pump blood. Other causes include coronary artery disease, cardiomyopathy – thickened heart muscle, scarring from previous heart attack, valvular heart disease, congenital heart disease, electrophysiological abnormalities, pulmonary embolism. Age [above 45 for men and above 55 for women], previous episode of cardiac arrest or a family history of cardiac arrest, a personal or family history of other forms of heart disease are the people at higher risk. Drug abuse, electrical shock, immersion in cold water, physical stress such as intense physical activity, severe blood loss, and severe lack of oxygen are the additional risk factors for sudden cardiac arrest. Men are 2 – 3 times more affected than women.
Clinical presentation
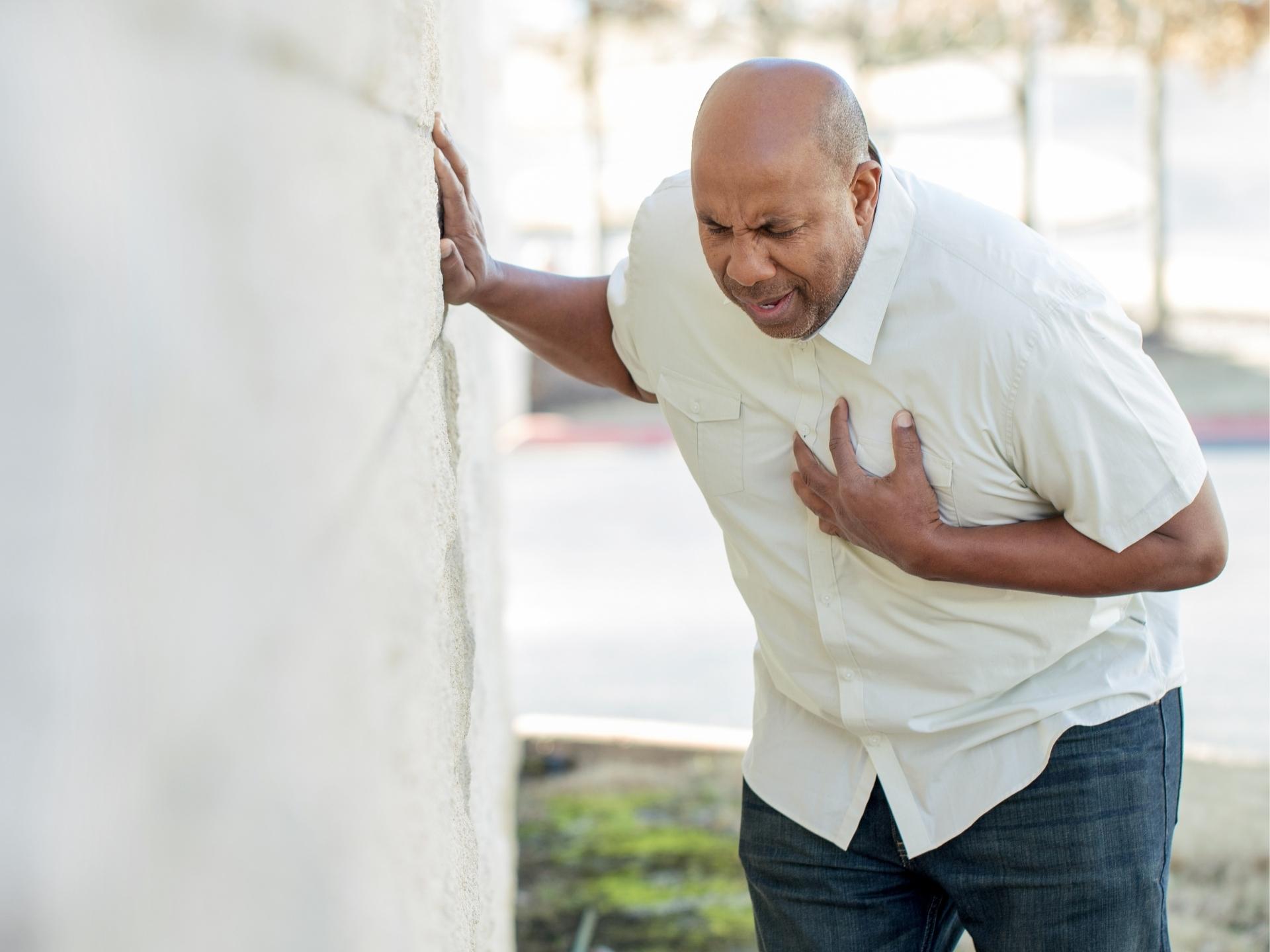
Sudden cardiac arrest occurs without any warning signs or symptoms. Patient presents with loss of consciousness, sudden collapse, no pulse, no breathing. Sometimes preceding symptoms like dizziness, fainting, blackouts, sweating, chest pain, shortness of breath, weakness, palpitations may be present. It differs from heart attack in which there is insufficient blood supply to the heart muscle, but heart continues to beat which eventually if not treated leads to cardiac arrest.
Investigation
Medical history by the patient and Clinical examination by the doctor helps in diagnosis. Since sudden cardiac arrest occurs without any warning signs, it is never diagnosed when it is happening. After the episode the doctor would like to investigate to find out the cause and prevent it in future. Doctor recommends an electrocardiogram, Blood tests to check cardiac enzymes, serum electrolytes, drug test, and hormonal levels. Imaging test include chest x-ray, echocardiogram, Ejection fraction test, Angiogram.
Treatment
Sudden cardiac arrest is a medical emergency. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation [CPR] and defibrillation of the heart is done to revive the patient. To prevent future attacks doctor may consider certain medical treatment. Implantable cardioverter-defibrillator, Coronary angioplasty, Coronary bypass surgery, Radiofrequency catheter ablation, Corrective heart surgery will contribute further to the treatment.