Causes and risk factors
The exact cause of cancer is not known, but various risk factors or predisposing factors have been put forth. It is found that the cells (follicular and parafollicular) undergo an uncontrolled and abnormal proliferation which gives rise to formation of tumors. Genetic predisposition is one of the major causes. Hereditary plays a major role. People with weak immune system are more prone for cancer. Exposure to ionizing radiation is one of the major causes of thyroid cancer. Hence radiation treatment on head or neck poses a risk for thyroid cancer. A low iodine diet is another risk factor for thyroid cancer. Hence it is more prevalent in areas where there is significantly low iodine content. Thyroid diseases like goiter, hypo and hyper thyroidism along with thyroiditis poses also contribute to thyroid cancer.
Clinical presentation:
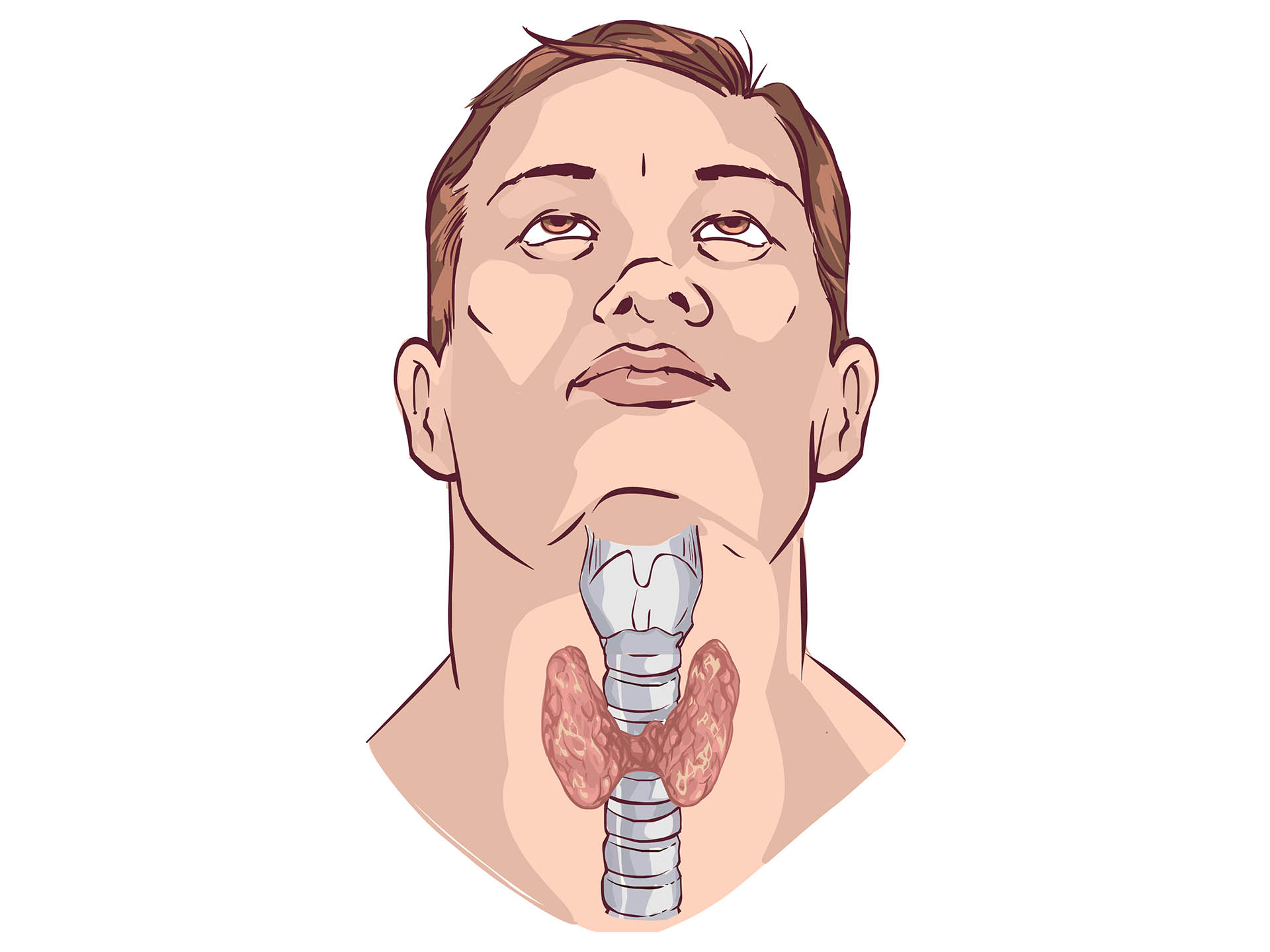
There are different types of thyroid cancers. Among all papillary thyroid cancer is the most common accounting for about 75-80% of cancer affections. Symptoms appear gradually. A lump or swelling in the neck is seen. It grows gradually. This growth causes compression of the underlying structure, leading to difficulty in swallowing, hoarseness of voice, breathing difficulty. It can evoke cough also. Pain in the neck radiating to ear can be felt. Various other symptoms like sexual dysfunction, irregularities in menstrual cycle in females, gynacomastia, altered bowel habit, loss of appetite are seen due to alteration in the hormonal levels.Bodyache, fatigue, tenderness all over the body are the other associated symptoms .The cancerous cells can cause metastasis in various other organs of the body leading to variety of symptoms.
Investigations:
Diagnosis is done on the basis of symptoms narrated by the patient and the examination carried out by the doctor. Certain investigations like routine blood test; Blood markers for cancer are advised. Ultrasound scanning of the thyroid gland is suggested. On detection of any abnormalities in the thyroid biopsy is recommended. A radioiodine scan will aid in diagnosis. A complete thyroid profile is recommended .A complete scan (PET scan) of the body along with other routine investigations can also be done for metastasis.
Treatment:
Depending upon the extend and stages of cancer the treatment is planned. Various surgical approaches can be adopted. Depending upon the extent of the cancer. Thyroid lobectomy of thyroidectomy is recommended. Radiation therapy is used. Targeted chemotherapy and immunotherapy agents are administered. Medications for stimulating the thyroid hormones are also prescribed.
Recent update:
In an article published online by an American cancer society states that adolescents and young adults who develop thyroid cancer as a secondary cancer have a significantly greater risk of dying than those with primary thyroid cancer.