Causes and risk factors
Exact cause of polyp is unknown. But gene mutations can cause uncontrolled cell division causing polyps. Hormonal changes during menstrual cycle play an important role in development of polyps. Oestrogen hormone causes thickening of endometrium every month, is responsible for development of polyp. High risk women include those between age of 40 and 50 years, post menopausal women. Certain medications used for treating breast cancer, also have the risk of causing uterine polyps. Other risk factors include obesity, high blood pressure.
Clinical presentation
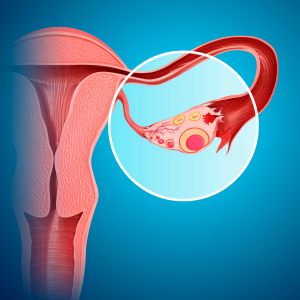
Many times patient is asymptomatic. The polyps are rich in blood supply. Sometimes these polyps rupture and cause unexplained bleeding from vagina. Common symptoms include irregular menstrual bleeding – menorrhagia or metrorragia, bleeding in between periods, unexplained vaginal bleeding in post menopausal women. If the polyps occur before menopause, in child bearing age group, it can cause infertility.
Investigation
Medical history by the patient and Clinical examination by the gynaecologist helps in diagnosis. An ultrasound pelvic examination is recommended. D and C – dilatation and curettage is useful in case of small polyps. Suspecting larger polyp, transvaginal ultrasound, hysteroscopy are done. Pap smear may be required to rule out cervical cancer. Hysterosalpingogram is useful. Tissue biopsy is advised to rule out malignancy.
Treatment
No treatment is required for asymptomatic patients. Regular check up and observation is needed. Certain medications can cause shrinkage of polyps. Surgical treatment consists of removal of polyps by hysteroscopy. If the polyps are suspected to be malignant, hysterectomy is required.
Other Modes of treatment
The other modes of treatment can also be effective in treating uterine polyp. Homoeopathy is a science which deals with individualization considers a person in a holistic way. This science can be helpful in combating the symptoms. Similarly the ayurvedic system of medicine which uses herbal medicines and synthetic derivates are also found to be effective in treating uterine polyp.





![Lobular Carcinoma In Situ [LCIS]](https://moho.loopshell.com/read/wp-content/uploads/2022/01/Lobular-Carcinoma-In-Situ-Lcis-300x300.png)