The normal amount of hair growth is determined on the basis of age, sex, and ethnicity of the individual. Only rare cases involve the presence of androgen hormone in these cases. In hirsutism, which is the growth of excessive hair in women, there is the participation of the androgen hormone. The symptoms of hirsutism include growth of hair on the upper lips, chin, and other areas where men encounter hair growth.
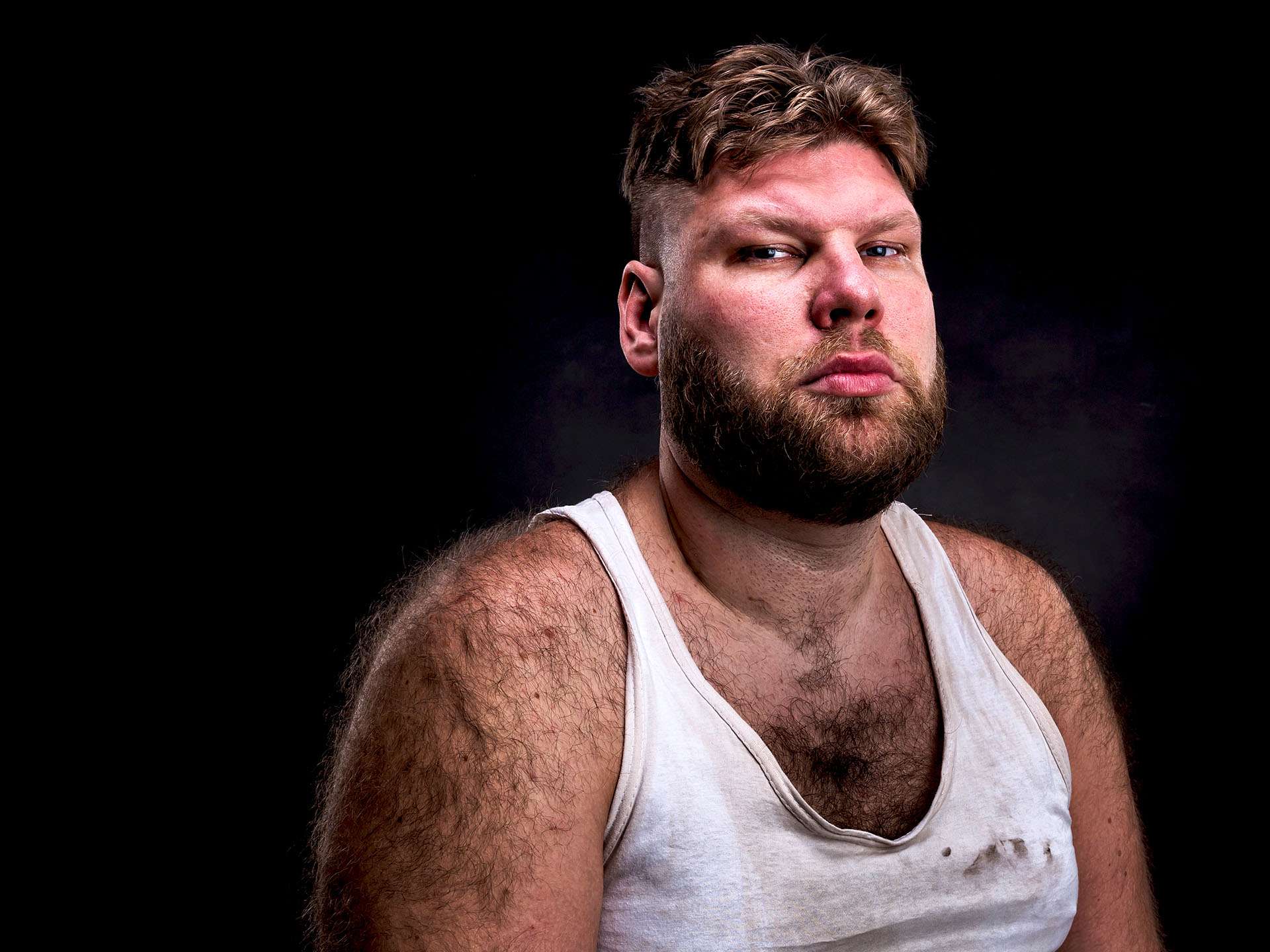
While hypertrichosis is generally a cosmetic issue, it is often indicative of a deeper medical issue which can be brought to the fore post diagnosis and can be treated accordingly. There can be two forms of hypertrichosis: generalized and localized. Generalized hypertrichosis refers to the excessive growth of hair all over the body. Localized hypertrichosis is characterized by abnormal hair growth at a singular or few body sites. Both these types can either be congenital (occurring from birth) or acquired (developing over time).
There are three types of hairs which develop in the human body. The lanugo hair refers to silky, long, and light-colored hair, which usually grows on the embryos of the womb. These are generally given up between the 7th month of pregnancy and the first months post birth. Vellus hair refers to the shorter and non-pigmented hair that replaces the lanugo hair. These occur in all parts of the body apart from eyebrows and scalp. Lastly, terminal hair is the name given to pigmented, thicker, and the coarser type of hair, e.g., covering the eyebrows and scalp. These also are found in the groin and underarm region after an individual undergoes puberty. In case of generalized hypertrichosis, there can be engagement of all the three types of hair. On the other hand, localized hypertrichosis is generally marked by the growth of vellus hair into terminal hair.
As a form of treatment, depilation uses different types of thioglycolates. These are used in perming generally and involve the dissolution of hair shaft while leaving the hair bulb intact. The effect generally lasts for two weeks.
Generalized congenital hypertrichosis is a rare inherited disorder where the lanugo hair that is generally given up after birth continues to grow on the whole body of the infant and with low intensity only on the palms and soles. Ears, face, and shoulders are the most vulnerable areas. In case of acquired generalized hypertrichosis, the common causes are the use of drugs like minoxidil, phenytoin, and cyclosporine A. The condition is generally resolved after the discontinuation of the drug use. This could also be caused due to malnutrition, head injury, AIDS, and starvation. Localized congenital hypertrichosis is present in a small number of body sites including ears, back, elbows, and nevi. Spinal defects or neural damage could also be the cause of excessive hair growth on the back. Localized acquired hypertrichosis is caused by diverse type of injuries including irritation, trauma, or inflammation. The response to the local injury might include the transition of the vellus hair into coarse terminal ones.
While in many of the cases of acquired hypertrichosis, cure is not possible, cosmetic treatment can be sought for congenital hypertrichosis. No singular treatment has been found for hypertrichosis until now.
The most suitable procedure of treatment depends upon the site, intensity, and type of growth and, especially, the preferences of the patient.
The most common treatments include electrolysis, depilation, shaving, laser removal, plucking, and epilation. Science is moving towards finding ways to permanently remove hair in cases of hypertrichosis. The highest hopes are held with electrolysis and laser treatment.