Causes
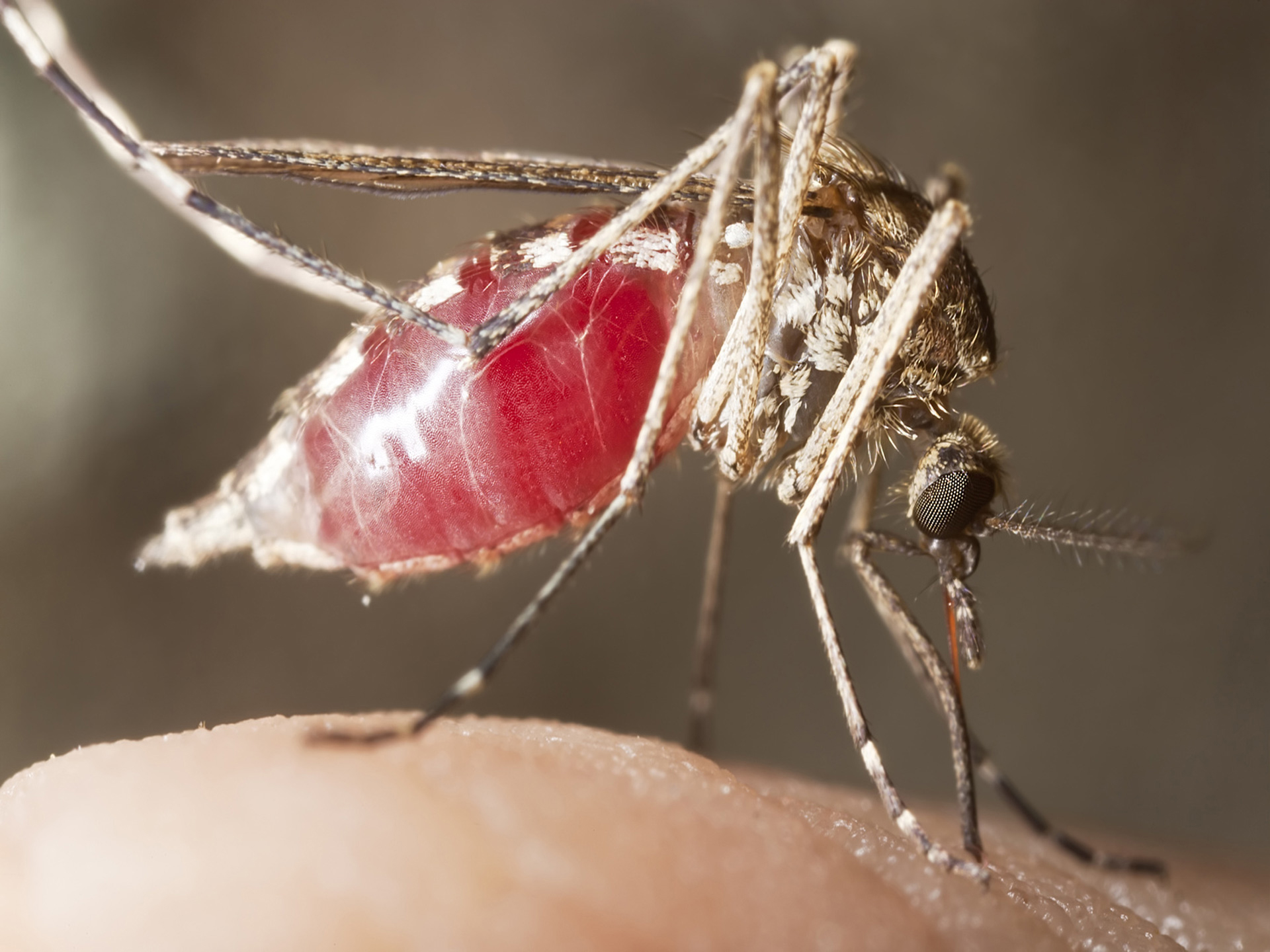
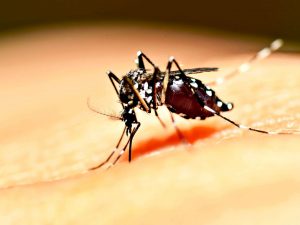
Malaria is caused by a parasite that is passed from one human to another by the bite of infected mosquitoes- called Anopheles. It can transfer to a child from the mother during pregnancy.
Symptoms
First symptoms usually occur within 10 days to 4 weeks after infection, but can appear as early as 8 days or as long as a year after infection in cycles of 48 to 72 hours.
FEVER: Rise in temperature, chills or shivering, sweating, nausea with vomiting, joint pain, muscle ache and headache, especially during evenings is a strong malaria symptom.
Severe symptoms: Anaemia, convulsions, bloody stools, jaundice, coma.
Diagnosis:
- Based on signs and symptoms.
- On physical examination by doctor- liver or spleen might be enlarged.
- Tests: Rapid malarial test.
- Malarial smears taken at 6-12 hours intervals, during fever stage confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment:
- See a doctor.
- Anti-malarial drugs – Choloquines (commonly used).
Complications: Respiratory distress, pulmonary oedema, hemolytic anemia-destruction of blood cells, liver or kidney failure, meningitis.
Prevention: Eliminate mosquito-bites by proper sanitation and prevention of mosquito breeding, use mosquito repellents, wear protective clothing over arms and legs, use screens on windows. Travellers and pregnant women should take preventive medications.