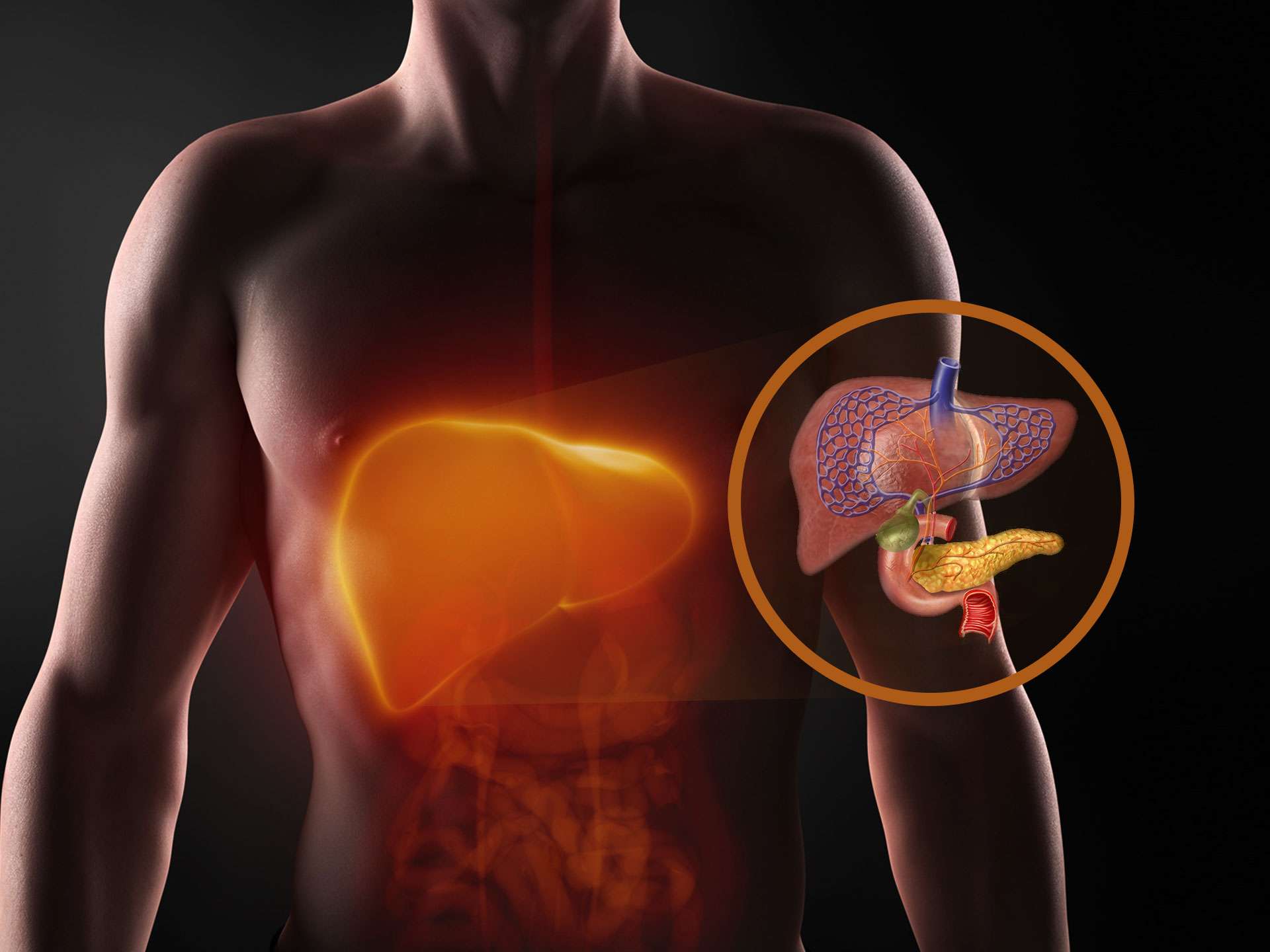
There are two types of liver diseases, acute and chronic. While the acute form develops over months, the chronic form generally has its onset several years ago. There are two major ways in which alcohol can injure your liver: Oxidative tension and toxins in the gut bacteria.
Oxidative tension happens when the cells of the liver are damaged in the process of decomposing alcohol. This results in scarring and inflammation of the liver. Alcohol can indirectly harm your liver by allowing toxins to enter your liver due to its negative impact on the intestines.
There is no consensus on how much drinking can be labeled as being ‘too much’ as different bodies possess varying immunity and strength. However, four factors play a major role in determining the well-being of your body and the effect of alcohol on it: Dependence level on alcohol, sex of the person, weight, and genetic dispositions.
It is recommended that men must not have more than 8 units of alcohol (which is approximately 4 pints) per day and women should not drink more than 5 units per day.
Fatty liver is the initial stage of onset of liver disease. The symptoms include loss of appetite, discomfort in the abdominal region, and fatigue. A blood test will confirm the condition.
Other symptoms also include vomiting, nausea, and diarrhea. As the condition progresses, one can have the following signs: itching, jaundice, liver cancer, blood in vomit, increased sensitivity to drugs and alcohol, fatigue; inflammation of leg, abdomen, and ankles, as well as bleeding in the gut area. Symptoms of nervous system like dizziness, numbness in legs and issues related to memory, mood, and thought process may also present itself.
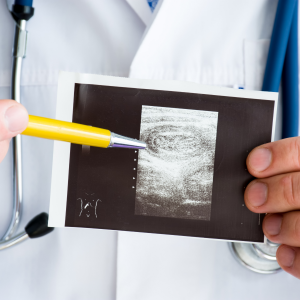
Three main tests are done to diagnose the condition: Complete blood count, liver function test, and liver biopsy. In order to eliminate other diseases arising in the differential diagnosis, the patient might undergo blood test for suspected causes of liver illness and/or abdominal ultrasound as well as CT scan of abdomen.
Did you know that over 35% of the people around the world die due to liver diseases? It has also been found that over the years the age of those suffering from liver diseases have been falling into the early 40s range.
The essential part of the treatment is to stop drinking. In case liver cirrhosis has not developed yet, the liver will have the capacity to restore itself to health on its own with minimal medical help. One can also consider alcohol rehabilitation program/counseling. In order to avoid malnutrition, multivitamins are suggested, specifically folic acid and vitamin B-complex. In extreme cases of liver diseases, one could be considered for transplantation of liver, provided the patient has given up drinking.