A ready reckoner on age – Apt diet for kids
It is essential to feed kids on an age-appropriate diet to ensure adequate nutrition proper growth and development.

Age: Birth to 4 months:
1. Only breast milk is required and sufficient for infants during the first 4-6 months after birth to fulfil the nutritional needs. It is recommended to feed infants on breast milk for the first six months of life. A fortified formula can adequately meet an infant's needs in case breastfeeding is not possible due to any reasons. 2. If breastfeeding, a newborn may need to nurse 8 to 12 times a day or every 2 to 4 hours. It might reduce to 4 to 6 times in a day by fourth month. The quantity of breast milk consumed at each feeding will increase by now. 3. Avoid giving honey to an infant, as immature GI is incapable of digesting it and it may contain the spores that cause botulism (poisoning). The body’s immune system at this age is not fully developed to fight off this disease.
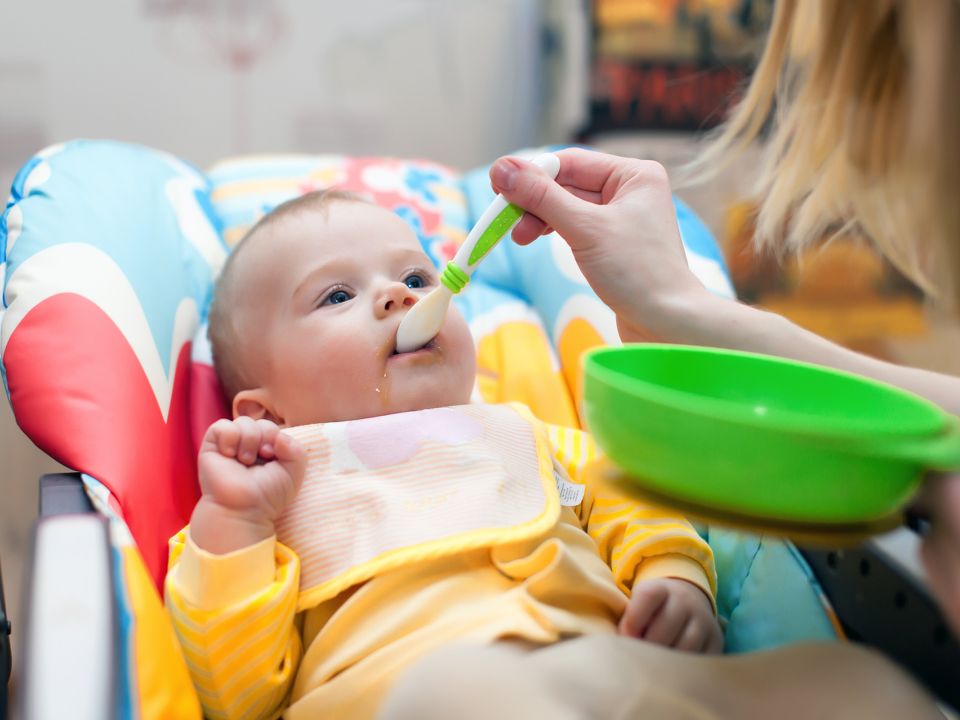

Age: 4 to 6 months
1. By 4 to 6 months of age, baby should be given 500 to 1000 ml of formula, and is usually ready for transition to solid foods. Starting solids too soon may lead to choking if they are not physically ready. 2. Developmental milestones that suggest that the baby is ready for solids: Birth weight is doubled; the infant has good head and neck control and can sit up with some support; shows interest in food when others are eating, turns head away from food and doesn’t open mouth when full. 3. Introduce single new cereal every week. This will help to rule out intolerance. 4. Caution: Do not put a child to bed with a bottle as this can cause "bottle mouth," resulting in tooth decay. Use plain water if a bottle is necessary.
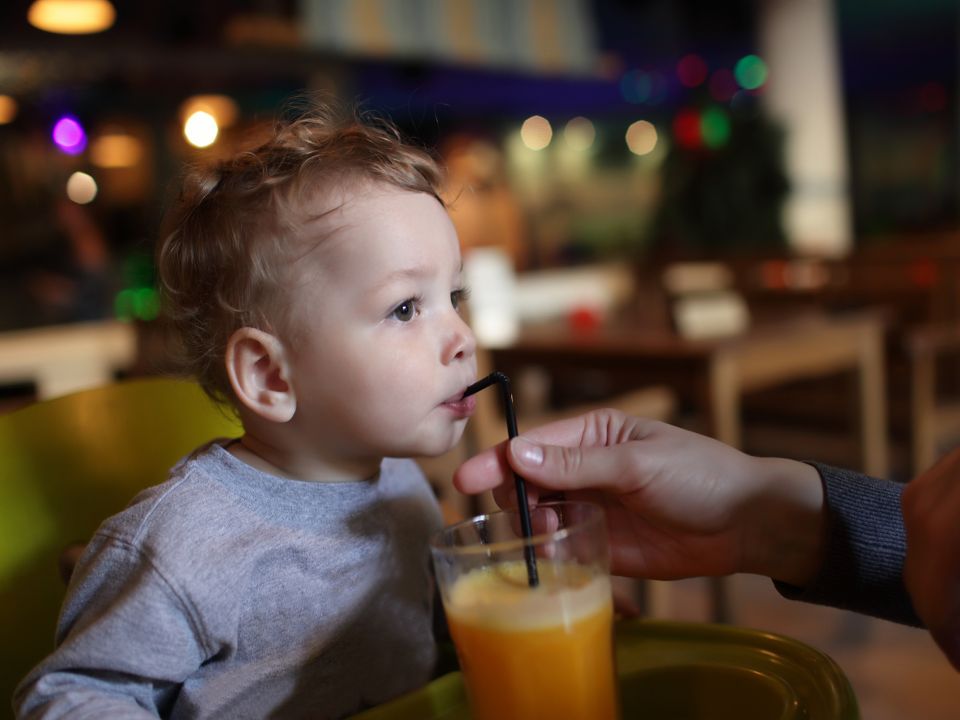

Age: 6 to 8 months:
1. Continue breast milk or formula about 3-4 times a day only after baby has tried a variety of different baby cereals. 2. Try fruit juices and strained fruits and vegetables. Introduce one at a time waiting two to three days in between to rule out any allergic reaction. Begin with plain vegetables like carrots, sweet potatoes, beets and plain fruits like bananas, pears or melon. Amount of fruits and vegetables consumed per day will vary between 2 tablespoons and 2 cups depending on the size of your child and how well the child eats fruits and vegetables. 3. Try finger foods like soft cooked vegetables, very tiny peeled fruits. Avoid foods like apple chunks or slices, grapes, popcorn, nuts, seeds, etc which may cause choking. Salted or sweetened foods are not recommended. 4. This is a good time to introduce teething foods like toast strips, unsalted crackers, and teething biscuits gradually.
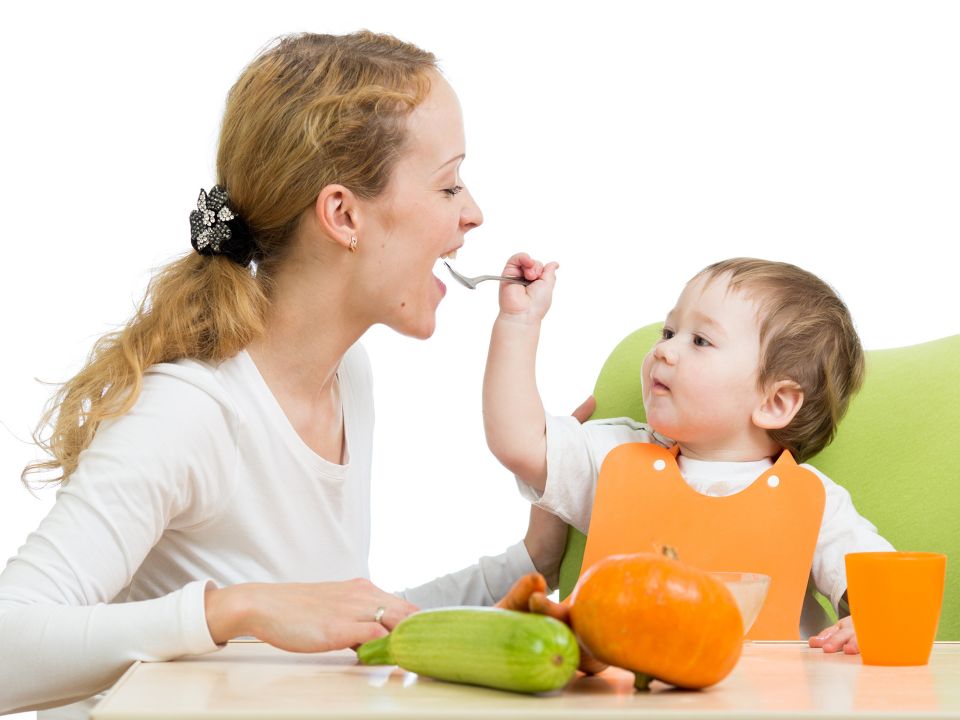

Age: 8 to 12 months:
1. Offer breast milk/ formula milk should be offered three to four times per day by now. Baby will be ready to try strained or finely chopped meats. Increase serving sizes of fruits and vegetables to 3-4 tablespoons, four times a day. Eggs can be given but not more than three times per week. Give only yolk until the baby is 1 year old, as some babies develop allergy to egg whites. 2. By the age of 1, most children are off the bottle. If the child still uses a bottle, it should contain water only.

Age: 1 year:
1. Replace breast milk or formula with whole milk. Kids below 2 years should not be given low-fat milk as they need the additional calories from fat to ensure proper growth and development. 2. Children under the age of 1 should not be given whole milk as it has been shown to cause anaemia. Cheese, cottage cheese, and yogurt may be given in very small amounts. 3. Provide a variety of foods to ensure adequate nutrition. Encourage snacking but on healthy foods as toddlers will now move around and won’t eat a lot a time. 4. Give water in between the feeds. 5. Avoid sweetened beverages as they spoil the appetite and cause tooth decay.