Degenerative disc disease- Everything that you should know
Gradual deterioration of the intervertebral disc(s) between the vertebrae is referred to as Degenerative Disc Disease or degenerative disc disorder. It is not a disease, but degeneration of the spinal discs with age or other factors such as injury. Read on to know more.
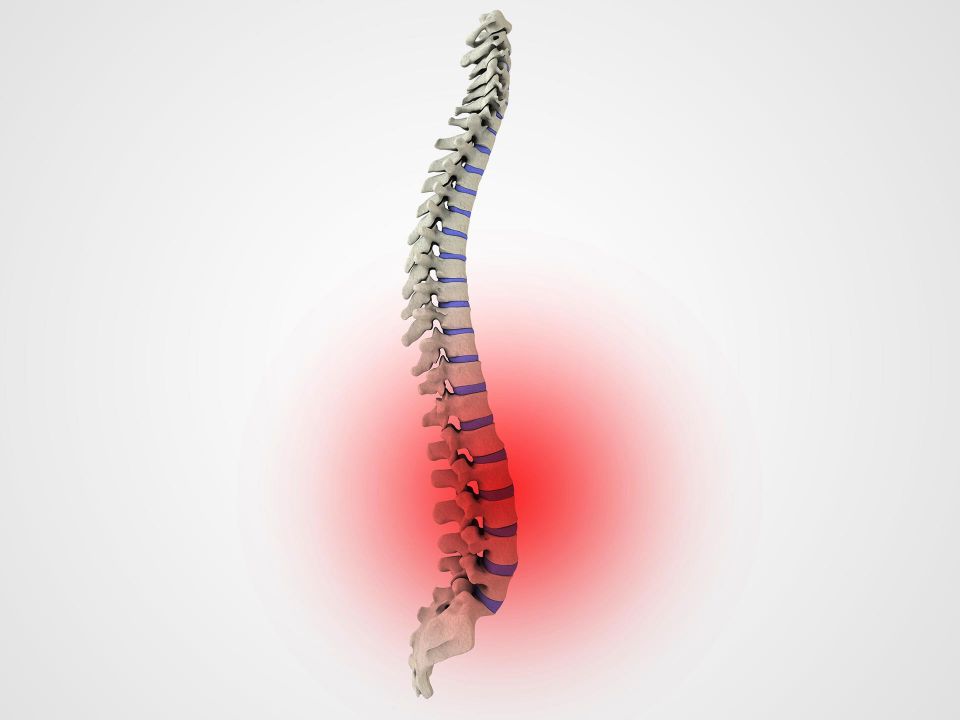
What is degenerative disc disease?
Gradual deterioration of the intervertebral disc(s) between the vertebrae is referred to as Degenerative Disc Disease or degenerative disc disorder (DDD). DDD is not an actual disease. It is the degeneration of the spinal discs with age or other factors such as injury.
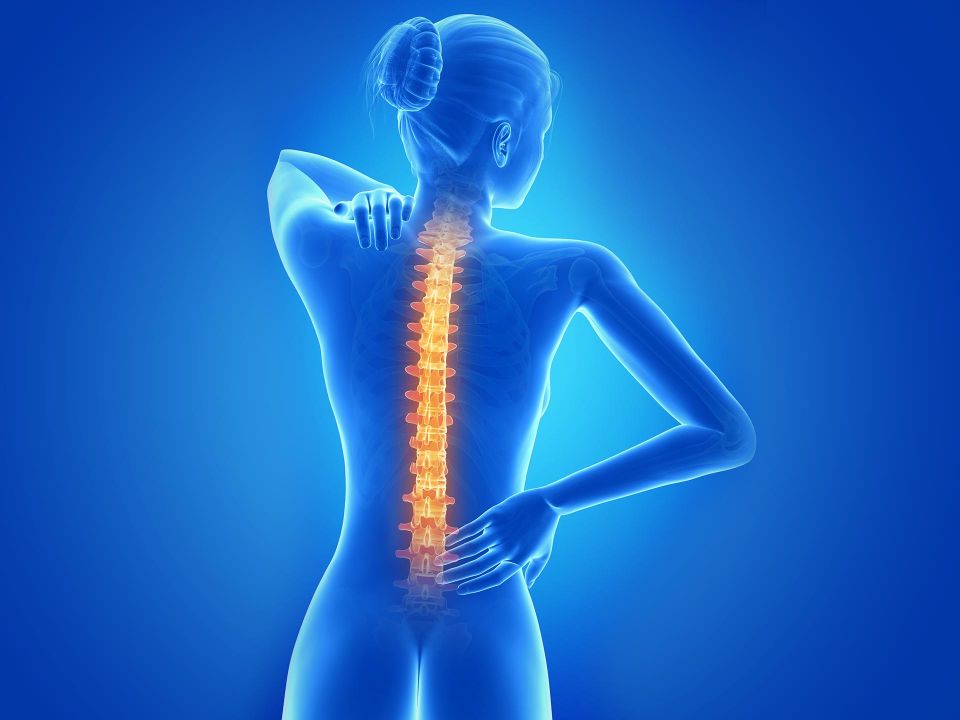
Where does it occur?
Anywhere in the spine but occurs most commonly in lumbar (lower back) and cervical (neck) regions.
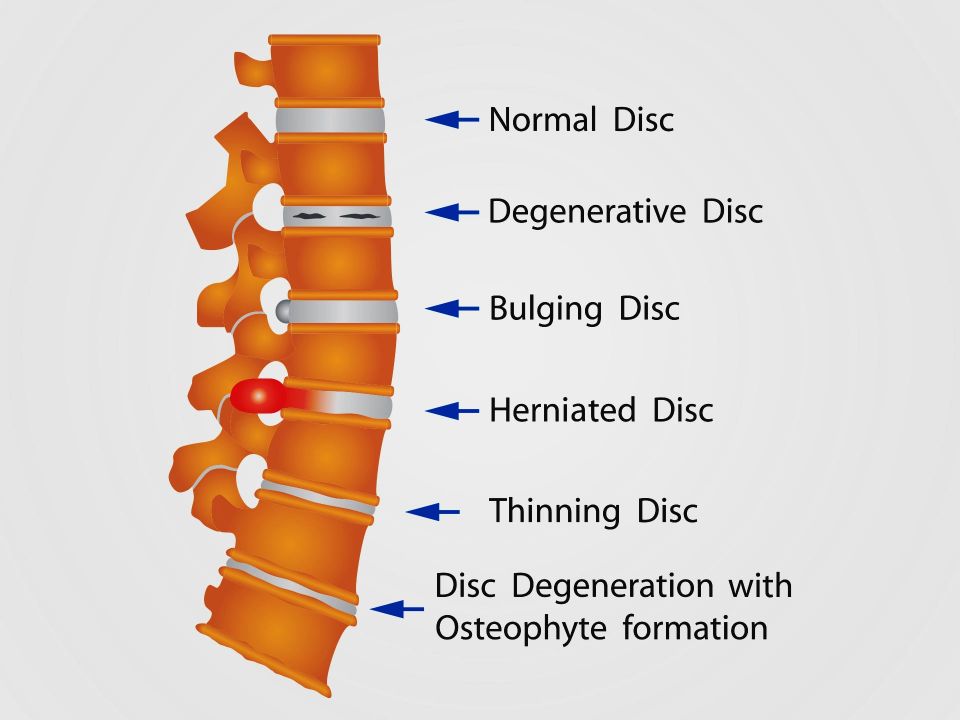
What does it appear as?
Degenerative Disc Disease can appear as one or more of the following: 1. Disc Space Narrowing: Due to the loss of water in the discs the distance between vertebrae begin to collapse. 2. Vacuum Disc: Accumulation of gas (principally nitrogen) with the crevices of the intervertebral discs or adjacent vertebrae. 3. End Plate Sclerosis: Increased thickening or density at the top and bottom of a vertebra. 4. Osteophyte formation: Commonly referred to as bone spurs or parrot beak. They are bony projections (calcification or new bone formation) that form along joint margins.
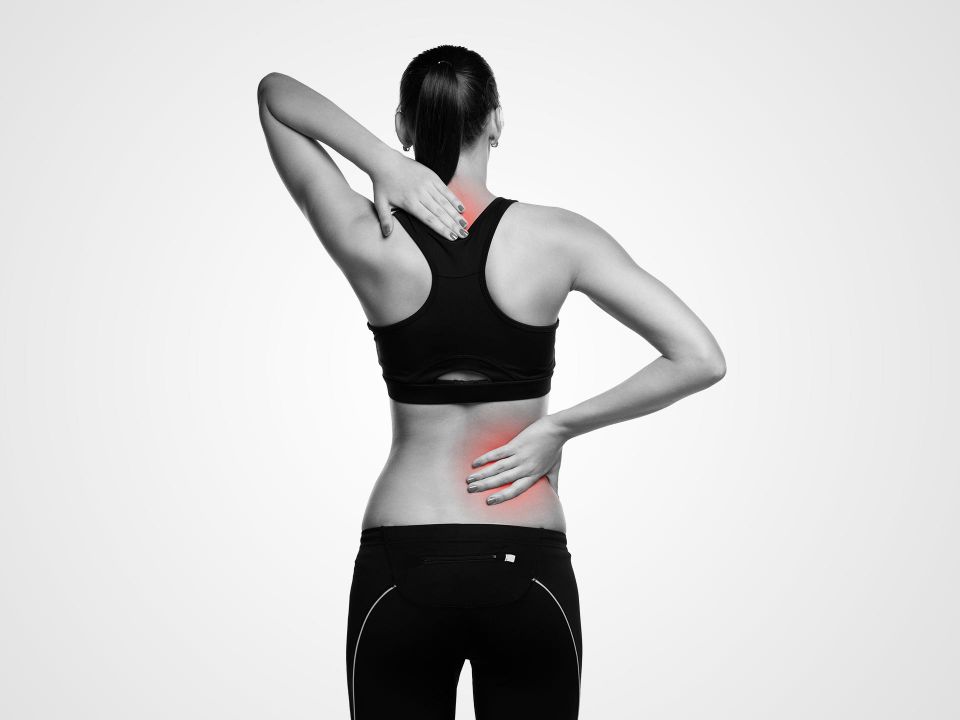
What does it result in?
1. Neck or lower back pain depending on the location where the damage has occurred and/or. 2. Osteoarthritis: breakdown of the tissue (cartilage) that protects and cushions joints. 3. Herniated disc: abnormal bulge or breaking open of a spinal disc. 4. Spinal stenosis: narrowing of the spinal canal.
What causes degenerative disc disease?
1. Age: Spinal discs degenerate with age. 2. Loss of fluid in the spinal discs leading to disc thinning. 3. Tiny tears or cracks: Cracks in the outer layer (annulus or capsule) of the disc forces disc nucleus out through the tear / crack leading to disc bulging, rupture or fragmentation.

Who is at risk?
Degenerative disc disease happens naturally with age. But the incidence is higher in. 1. Smokers. 2. Those Who Do Heavy Physical Work (Routine Heavy Lifting). 3. Obese People. 4. Those with sudden (acute) injury due to fall or accident.
What are the symptoms?
1. Pain in the neck or arm if the damage is cervical. 2. Pain in the back, buttock, or leg if the damage is in the lumbar. 3. Pain with incremental intensity during physical strain such as bending over, reaching up, or twisting or carrying weight.

How is it diagnosed?
Physical examinations are done to check. 1. Range of motion in affected area and for pain caused by movement. 2. Tenderness and any nerve-related changes, such as numbness, tingling, or weakness in the affected area. 3. Change in reflexes seen in associated nerve compressions.
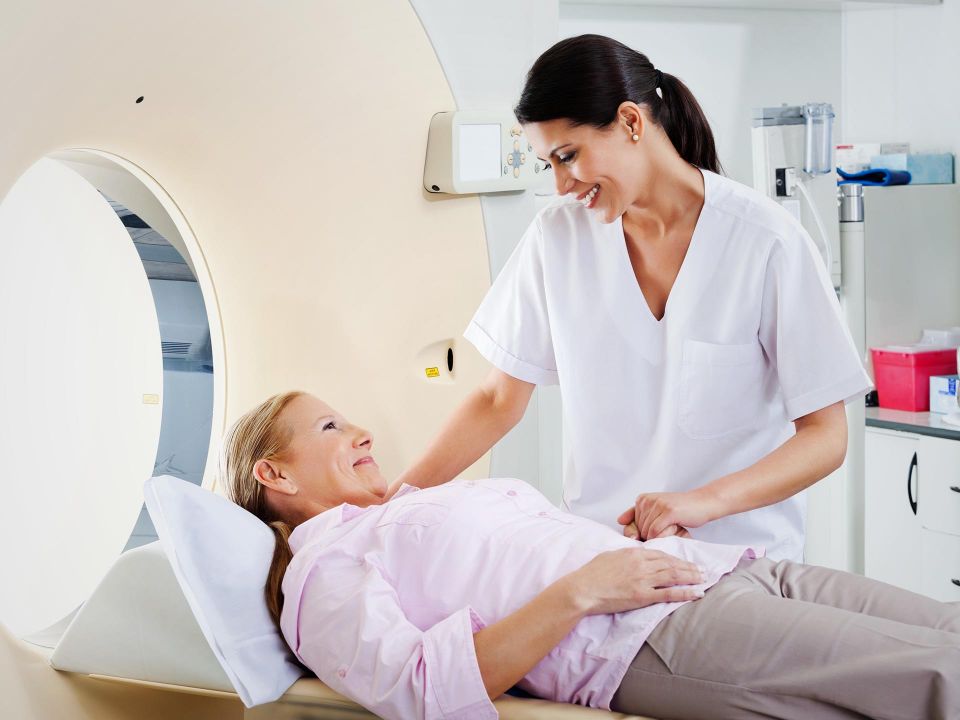
What are the tests used to diagnose degenerative disc disease?
Others tests include: 1.Imaging tests (e.g., x-rays, CT scan, MRI scan) 2. Electromyography (EMG) 3. Discography 4. Bone scan

How is it treated?
1. Cold or hot compresses on the affected area. 2. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory and analgesics are prescribed. 3. Physical therapy, chiropractic manipulative therapy (CMT) and other chiropractic treatments. 4. Osteopathic manipulation. 5. Traction. 6. Epidural corticosteroid injections. 7. Various surgical procedures.