Causative factors:
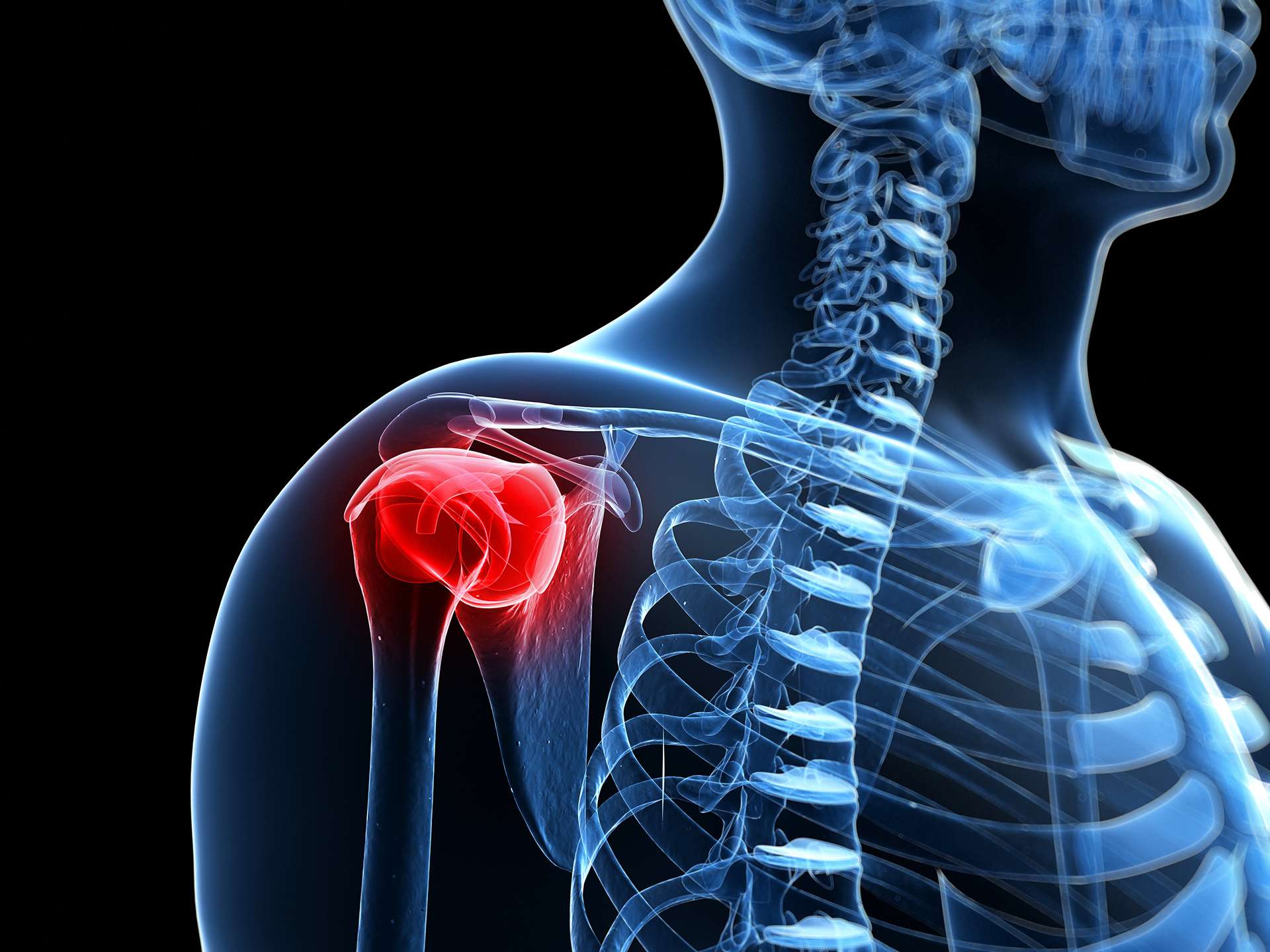
The bones, ligaments and tendons of shoulder joint are covered by a capsule. The capsule gradually thickens due to various factors to cause frozen shoulder.
Risk factors:
Various risk factors are associated with frozen shoulder:
- Age– People aged more than 40 years tend to develop frozen shoulder.
- Trauma– Injury of the shoulder joint or the nearby region may contribute to the development of shoulder joint.
- Diseases– Various diseases like diabetes, thyroid dysfunction, cardiovascular diseases may predispose frozen shoulder.
The diabetic connection
Diabetic patients have higher incidence of frozen shoulder. This is due to degenerative changes around the shoulder joint. Blood supply through the blood vessels is altered during diabetes. This poor blood circulation leads to cascade of pathological changes in and around the shoulder joint culminating into frozen shoulder.
It has also been observed that the incidence of pathological changes of the capsule covering the shoulder joint is 2 to 4 times higher in diabetic patients than in general population.
Test and diagnosis
The patients of frozen shoulder are evaluated by an orthopaedic surgeon. The initial diagnosis is made by the doctor by various physical examinations, although the doctor may ask for certain investigations in order to confirm the diagnosis. Imaging procedures like X-ray or MRI may be done to confirm the diagnosis and to rule out the other abnormalities.
Treatment
Treatment of frozen shoulder involves relief from pain and maintaining the range of movement of the shoulder joint.
Medication– Medications like painkillers are prescribed by the doctor for temporary relief from pain.
Physiotherapy– Regular physiotherapy with the help of a trained personnel helps to alleviate pain and improves the range of movement of the shoulder joint.
Surgical procedures- Short surgical procedures may be required for persistent cases of frozen shoulder. Following surgical procedures may be adopted:
- Steroid injections- Steroid preparations may be injected into the shoulder joint.
- Shoulder manipulation- Shoulder may be manipulated under general anesthesia to loosen the tightened tissue.
- Surgery- It is the last option. Surgery is undertaken by the orthopedic surgeon to remove the scarred tissue and adhesions around the shoulder joint.
Care of diabetes- Care of the underlying diabetes should be taken with proper medications and other measures.
Life style changes
After the initial phases of treatment, rehabilitation of the shoulder joint should be continued under the guidance of a trained physiotherapist. Subsequently the patient is advised to resume normal activities of the shoulder joint.
Prevention
Most common cause of frozen shoulder is immobility of the joint. Immobility may be due to an injury or disease processes like diabetes. So, proper treatment of the underlying disease and care of the shoulder joint is required for prevention of frozen shoulder joint.